Conjunction words are words that join ideas, sentences, or clauses together. They help us connect thoughts and show relationships like reason, contrast, choice, and time. In this blog post, you will learn 150+ A to Z conjunction words in English with pictures to help you understand how they are used in real sentences. Knowing conjunctions is very important for English learners because they make your speaking more natural, your writing more organized, and your reading easier to follow. When you understand how conjunctions work, you can build longer and more meaningful sentences. With regular practice, you will master how to connect ideas smoothly and improve your listening skills by recognizing how native speakers link their thoughts. Keep reading to explore the complete list from A to Z and strengthen your English step by step.
A to Z List of Conjunction Words
| Letter | Conjunction Words |
|---|---|
| A | and, after, although, as |
| B | because, before, but |
| C | consequently, considering |
| D | despite, during |
| E | either, even if, even though |
| F | for, furthermore |
| G | given that |
| H | however |
| I | if, in case, in order that |
| J | just as |
| K | knowing that |
| L | lest, like |
| M | moreover |
| N | nor, now that |
| O | or, otherwise |
| P | provided that |
| Q | rather than |
| R | regardless of |
| S | since, so, so that |
| T | than, though, till |
| U | unless, until |
| V | versus |
| W | while, whereas, whenever |
| X | — |
| Y | yet |
| Z | — |
List of Conjunctions in English
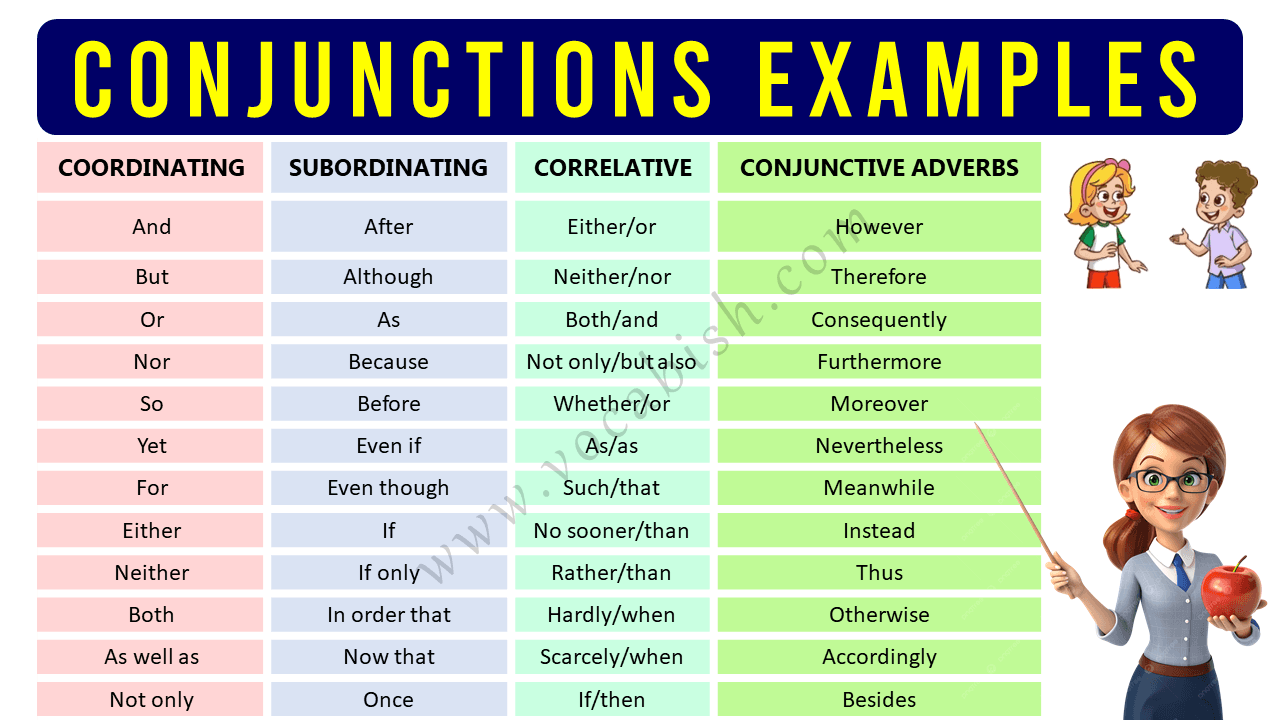
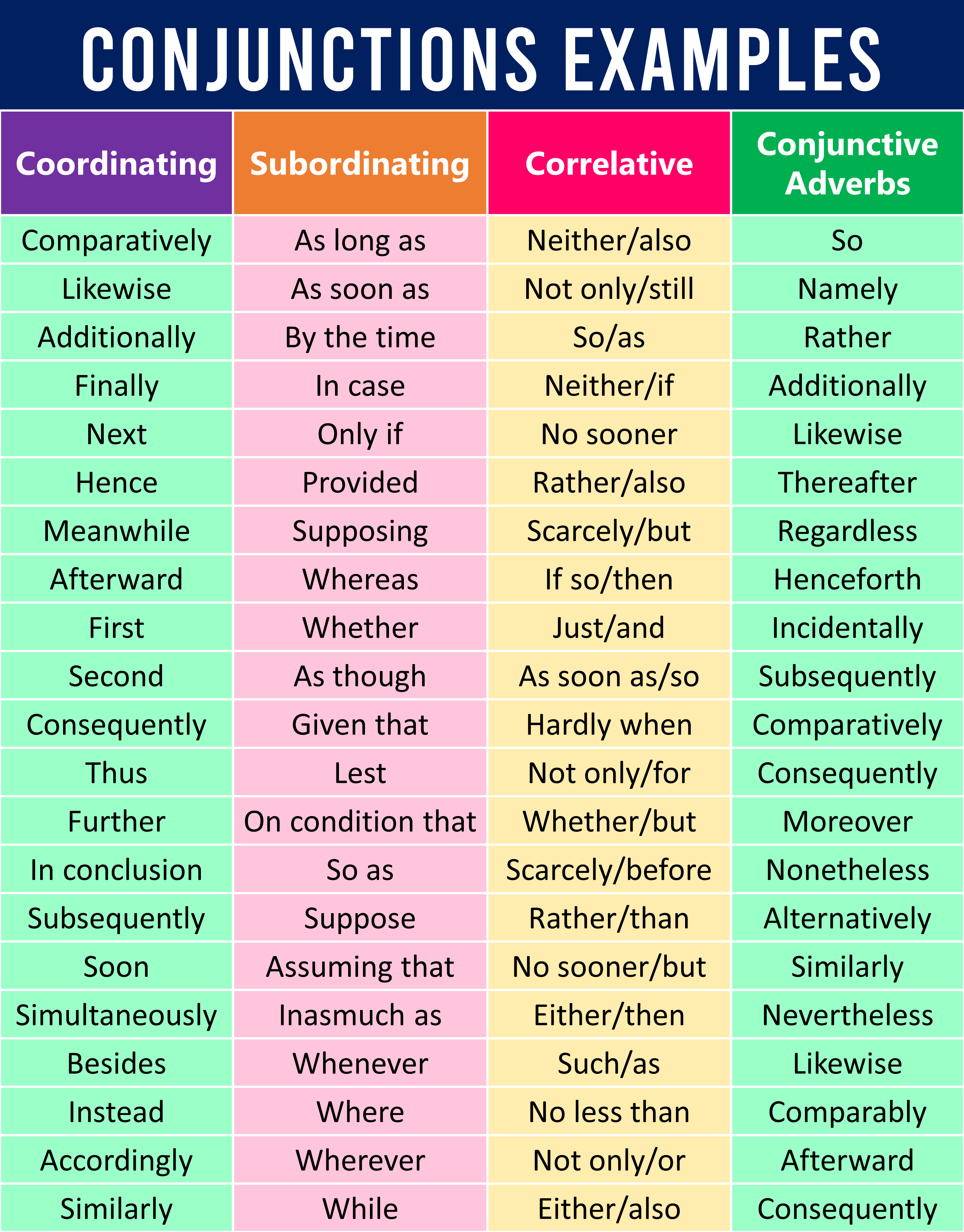
List of Coordinating Conjunctions
- And
- But
- Or
- Nor
- So
- Yet
- For
- Either
- Neither
- Both
- As well as
- Not only
- But also
- Still
- Even though
- Though
- Otherwise
- In fact
- However
- Moreover
- Furthermore
- Nevertheless
- Besides
- Instead
- Accordingly
- Similarly
- Comparatively
- Likewise
- Additionally
- Finally
- Next
- Hence
- Meanwhile
- Afterward
- First
- Second
- Consequently
- Thus
- Further
- In conclusion
- Subsequently
- Soon
- Simultaneously
- Then
- Therefore
- Beforehand
- Ultimately
- Wherefore
- Eventually
List of Subordinating Conjunctions
- After
- Although
- As
- Because
- Before
- Even if
- Even though
- If
- If only
- In order that
- Now that
- Once
- Provided that
- Rather than
- Since
- So that
- Than
- That
- Though
- Unless
- Until
- When
- Whenever
- Where
- Wherever
- While
- As long as
- As soon as
- By the time
- In case
- Only if
- Provided
- Supposing
- Whereas
- Whether
- As though
- Given that
- Lest
- On condition that
- So as
- Suppose
- Assuming that
- Inasmuch as
- Even so
- Whether or not
- Insofar as
- Just as
- Though
- Till
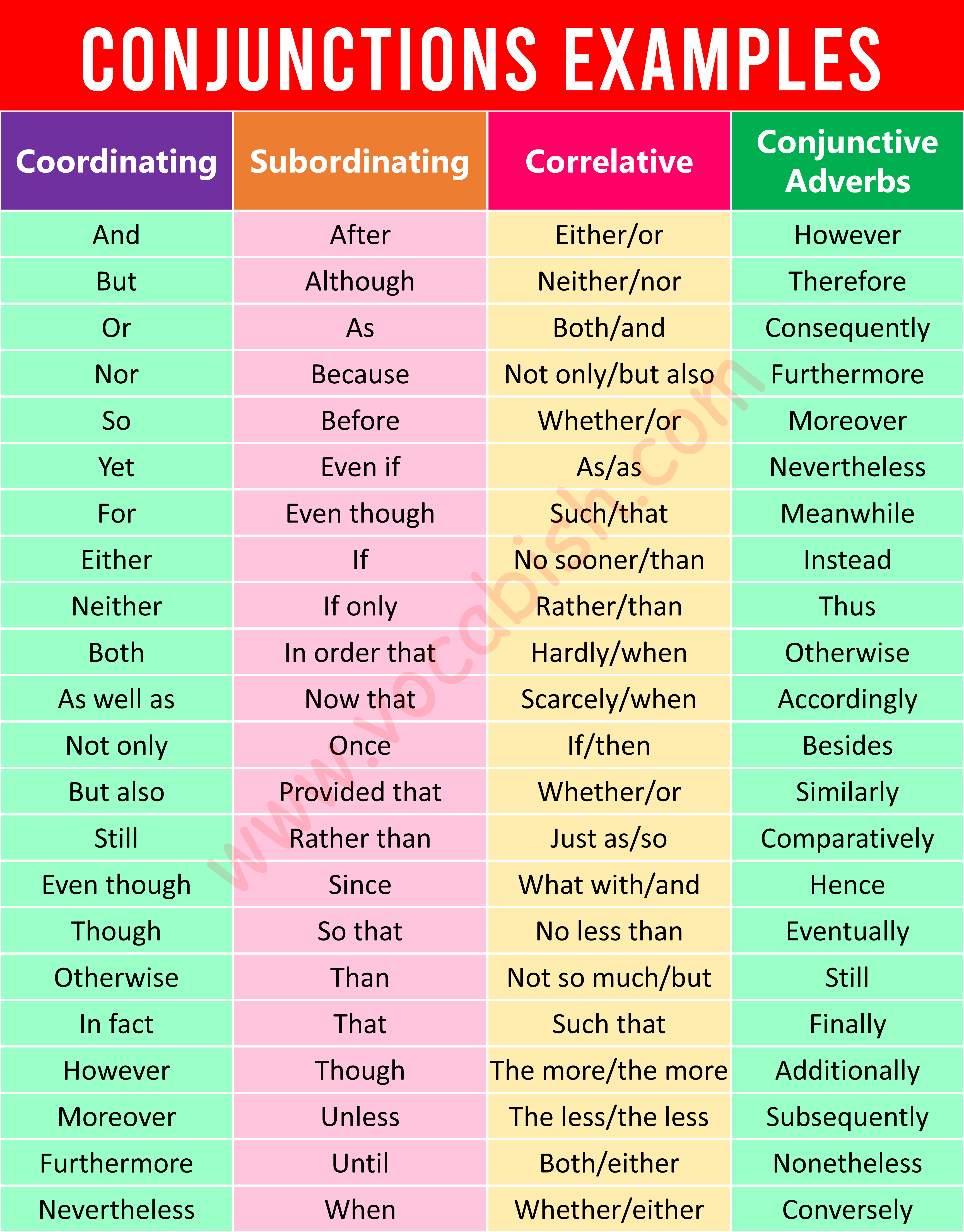
List of Correlative Conjunctions
- Either/or
- Neither/nor
- Both/and
- Not only/but also
- Whether/or
- As/as
- Such/that
- No sooner/than
- Rather/than
- Hardly/when
- Scarcely/when
- If/then
- Whether/or
- Just as/so
- What with/and
- No less than
- Not so much/but
- Such that
- The more/the more
- The less/the less
- Both/either
- Whether/either
- Such/as
- No less than
- Not only/or
- Either/also
- Neither/also
- Not only/still
- So/as
- Neither/if
- No sooner
- Rather/also
- Scarcely/but
- If so/then
- Just/and
- As soon as/so
- Hardly when
- Not only/for
- Whether/but
- Scarcely/before
- Rather/than
- No sooner/but
- Either/then
- If so/or
- No sooner/then
- Rather/not
- If and/but
- Not even/or
List of Conjunctive Adverbs
- However
- Therefore
- Consequently
- Furthermore
- Moreover
- Nevertheless
- Meanwhile
- Instead
- Thus
- Otherwise
- Accordingly
- Besides
- Similarly
- Comparatively
- Hence
- Meanwhile
- Accordingly
- Eventually
- Still
- Finally
- Additionally
- Subsequently
- Nonetheless
- Furthermore
- Conversely
- Likewise
- Comparably
- Afterward
- Consequently
- So
- Meanwhile
- Meanwhile
- Namely
- Rather
- Additionally
- Likewise
- Thereafter
- Regardless
- Henceforth
- Incidentally
- Subsequently
- Comparatively
- Accordingly
- Consequently
- Moreover
- Nonetheless
- Alternatively
- Similarly
- Nevertheless
Learning a list of conjunction words helps you join ideas and sentences clearly. Conjunctions make your English smooth, logical, and easy to understand.
FAQs
What is a conjunction in English grammar?
A conjunction is a word that joins words, phrases, or sentences together.
Example: I like tea and coffee.
What are 10 examples of conjunctions?
Here are 10 common conjunctions used in English:
and, but, or, because, so, although, while, if, when, unless.
What is the main use of conjunctions?
Conjunctions are used to connect ideas smoothly in a sentence and show the relationship between them.
Example: She was tired, but she kept working.
What are the 3 main types of conjunctions?
The three main types are:
- Coordinating Conjunctions → and, but, or
- Subordinating Conjunctions → because, although, when
- Correlative Conjunctions → either…or, neither…nor, both…and
How can I identify a conjunction in a sentence?
A conjunction links two parts of a sentence.
Example: I stayed home because it was raining.
Here, because connects the reason to the action.
Read More
- 500+ A to Z List of Nouns
- 250+ A to Z List of Pronouns
- 250 A to Z List of Preposition
- 300+ A to Z List of Adjectives