Adverb vocabulary is the group of English words that tell how, when, where, and how often an action happens. These words help learners add detail to sentences and express ideas more clearly. In this blog post, you will learn 450+ A to Z adverbs in English with their pictures. Each adverb is shown with meaning and use, so you can connect the word with real examples. When you practice adverbs, you improve speaking flow, read with better understanding, write more precise sentences, and listen with stronger focus. Keep reading to master how actions and events are described in English.
Here’s 450+ A to Z List of Adverbs in English:
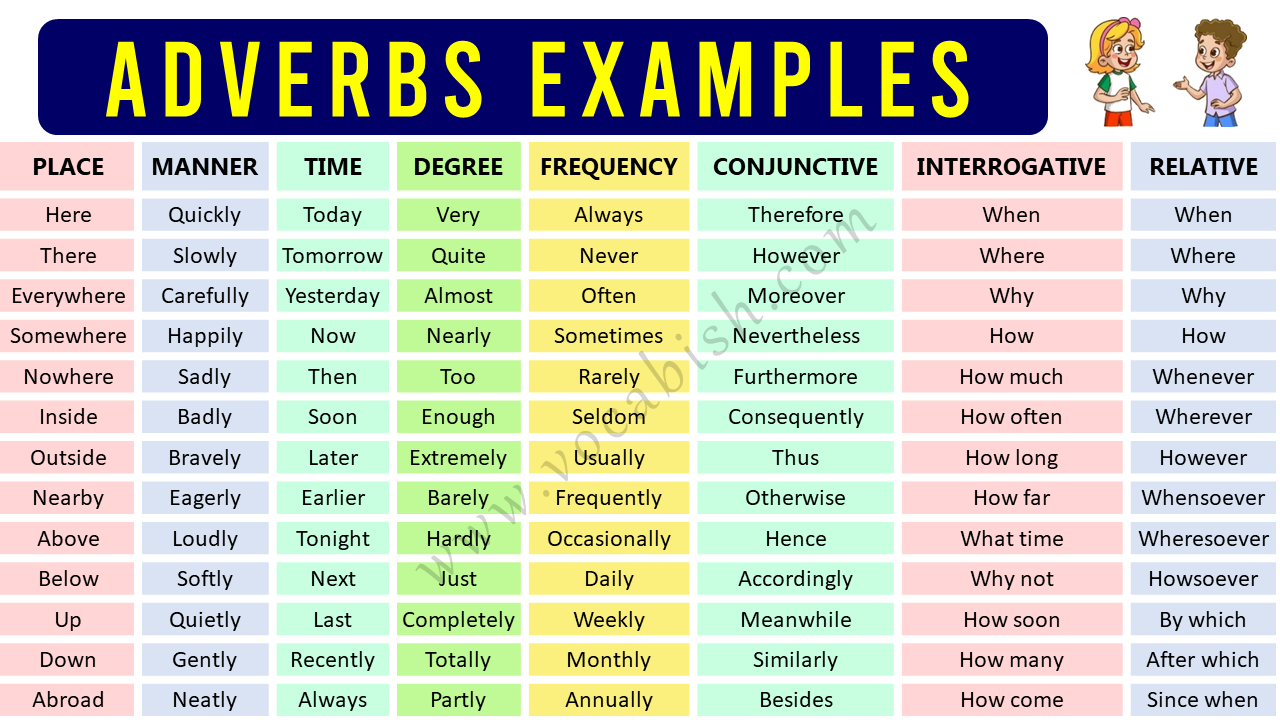
List of Adverbs in English
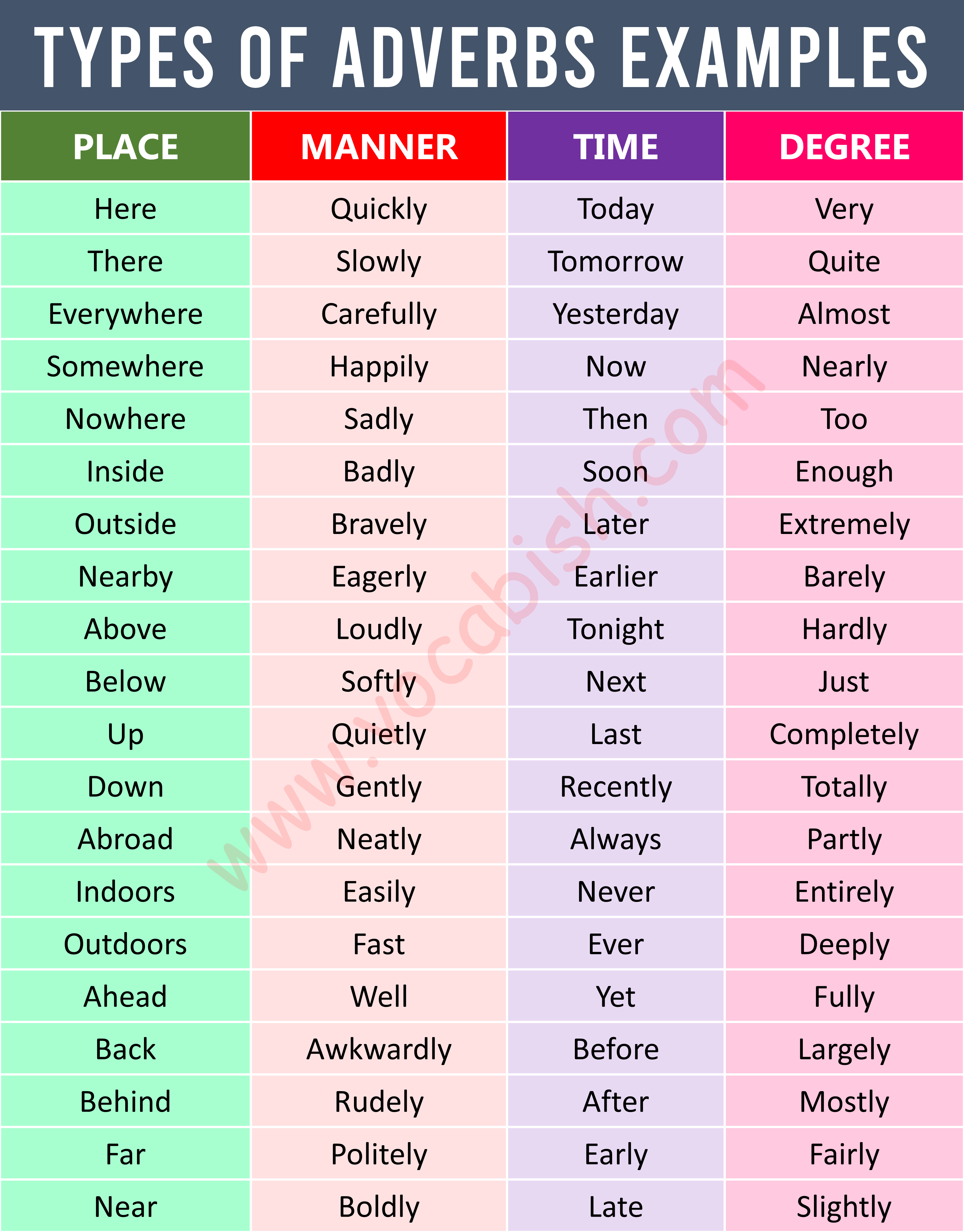
Adverb of Place
- Here
- There
- Everywhere
- Somewhere
- Nowhere
- Inside
- Outside
- Nearby
- Above
- Below
- Up
- Down
- Abroad
- Indoors
- Outdoors
- Ahead
- Back
- Behind
- Far
- Near
- Eastward
- Westward
- Northward
- Southward
- Left
- Right
- Forward
- Backward
- Hereabouts
- Out
- In
- Underground
- Overhead
- Anywhere
- Onward
- Upward
- Backwards
- Downstairs
- Upstairs
- Wherever
- Upwards
- Belowstairs
- Somewhere else
- Faraway
- Across
- Within
- Beyond
- Yonder
- Elsewhere
- Nearby
Adverb of Manner
- Quickly
- Slowly
- Carefully
- Happily
- Sadly
- Badly
- Bravely
- Eagerly
- Loudly
- Softly
- Quietly
- Gently
- Neatly
- Easily
- Fast
- Well
- Awkwardly
- Rudely
- Politely
- Boldly
- Wisely
- Cleverly
- Honestly
- Clearly
- Sharply
- Vividly
- Silently
- Smoothly
- Warmly
- Affectionately
- Angrily
- Cautiously
- Delicately
- Recklessly
- Furiously
- Calmly
- Passionately
- Truthfully
- Joyfully
- Graciously
- Nervously
- Tactfully
- Fearlessly
- Faithfully
- Grudgingly
- Solemnly
- Zealously
- Cheerfully
- Painfully
- Willingly
Adverb of Time
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Yesterday
- Now
- Then
- Soon
- Later
- Earlier
- Tonight
- Next
- Last
- Recently
- Always
- Never
- Ever
- Yet
- Before
- After
- Early
- Late
- Once
- Twice
- Sometime
- Again
- Already
- Eventually
- Finally
- In the morning
- In the afternoon
- In the evening
- Soon after
- Shortly
- By noon
- At midnight
- Since
- Nowadays
- Lately
- Just now
- By then
- Over time
- All day
- Any day
- From now on
- Instantly
- Previously
- Formerly
- At present
- In due time
- Later on
- Now and then
Adverb of Degree
- Very
- Quite
- Almost
- Nearly
- Too
- Enough
- Extremely
- Barely
- Hardly
- Just
- Completely
- Totally
- Partly
- Entirely
- Deeply
- Fully
- Largely
- Mostly
- Fairly
- Slightly
- Thoroughly
- Intensely
- Mildly
- Excessively
- Somewhat
- Absolutely
- Entirely
- Marginally
- Profoundly
- Radically
- Scarcely
- Utterly
- Purely
- Highly
- Significantly
- Sufficiently
- Decidedly
- Utmost
- Tremendously
- Vastly
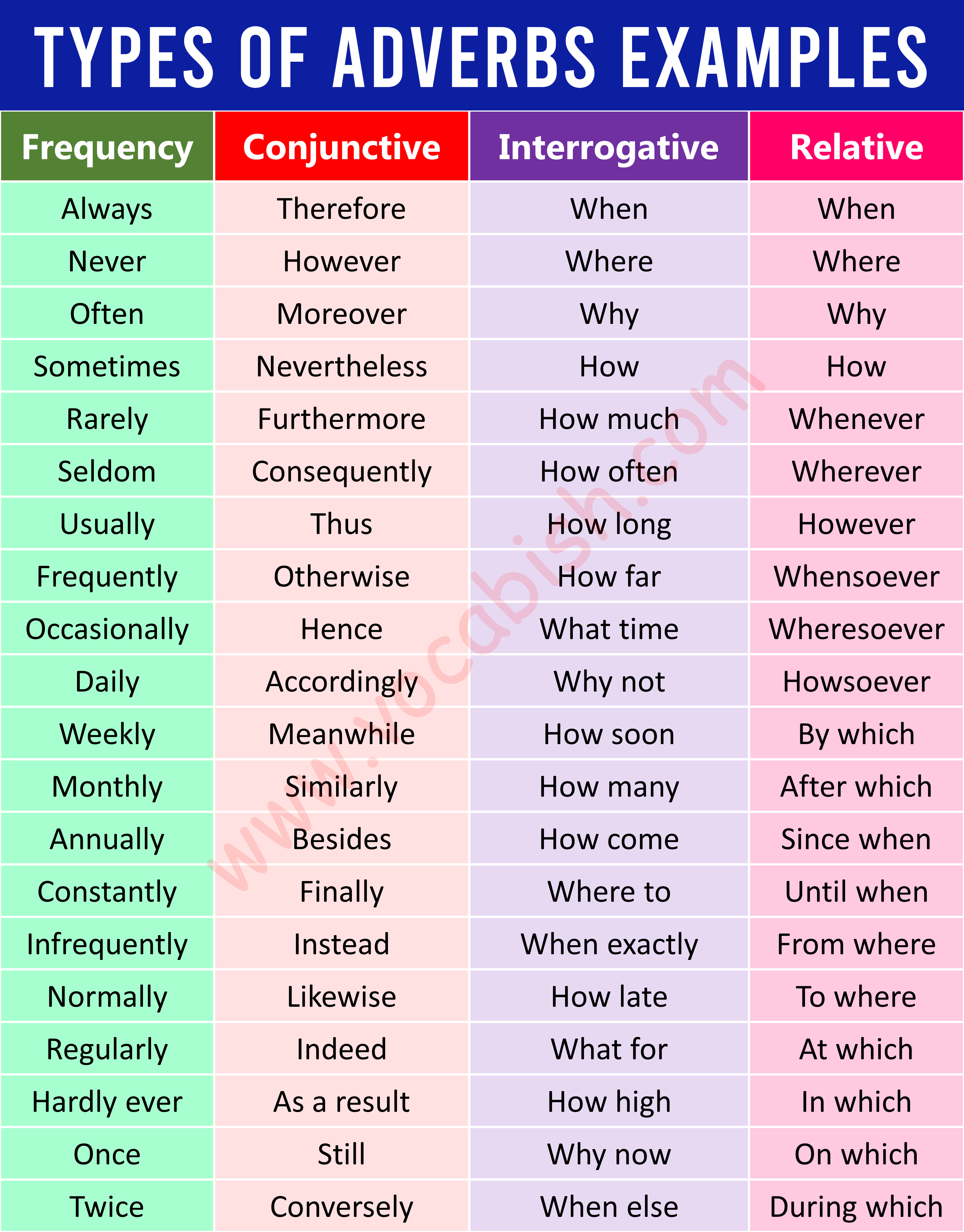
Adverb of Frequency
- Always
- Never
- Often
- Sometimes
- Rarely
- Seldom
- Usually
- Frequently
- Occasionally
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Annually
- Constantly
- Infrequently
- Normally
- Regularly
- Hardly ever
- Once
- Twice
- Thrice
- Again
- Repeatedly
- Every day
- Every week
- Once a week
- Every month
- Once in a while
- Per year
- Quarterly
- Every hour
- Yearly
- By day
- On occasion
- Per minute
- Most of the time
- Typically
- Sporadically
- Usually
- Constantly
Conjunctive Adverb
- Therefore
- However
- Moreover
- Nevertheless
- Furthermore
- Consequently
- Thus
- Otherwise
- Hence
- Accordingly
- Meanwhile
- Similarly
- Besides
- Finally
- Instead
- Likewise
- Indeed
- As a result
- Still
- Conversely
- Subsequently
- On the other hand
- Accordingly
- Nonetheless
- Next
- In fact
- Additionally
- Incidentally
- Similarly
- Afterwards
Interrogative Adverb
- When
- Where
- Why
- How
- How much
- How often
- How long
- How far
- What time
- Why not
- How soon
- How many
- How come
- Where to
- When exactly
- How late
- What for
- How high
- Why now
- When else
Relative Adverb
- When
- Where
- Why
- How
- Whenever
- Wherever
- However
- Whensoever
- Wheresoever
- Howsoever
- By which
- After which
- Since when
- Until when
- From where
- To where
- At which
- In which
- On which
- During which
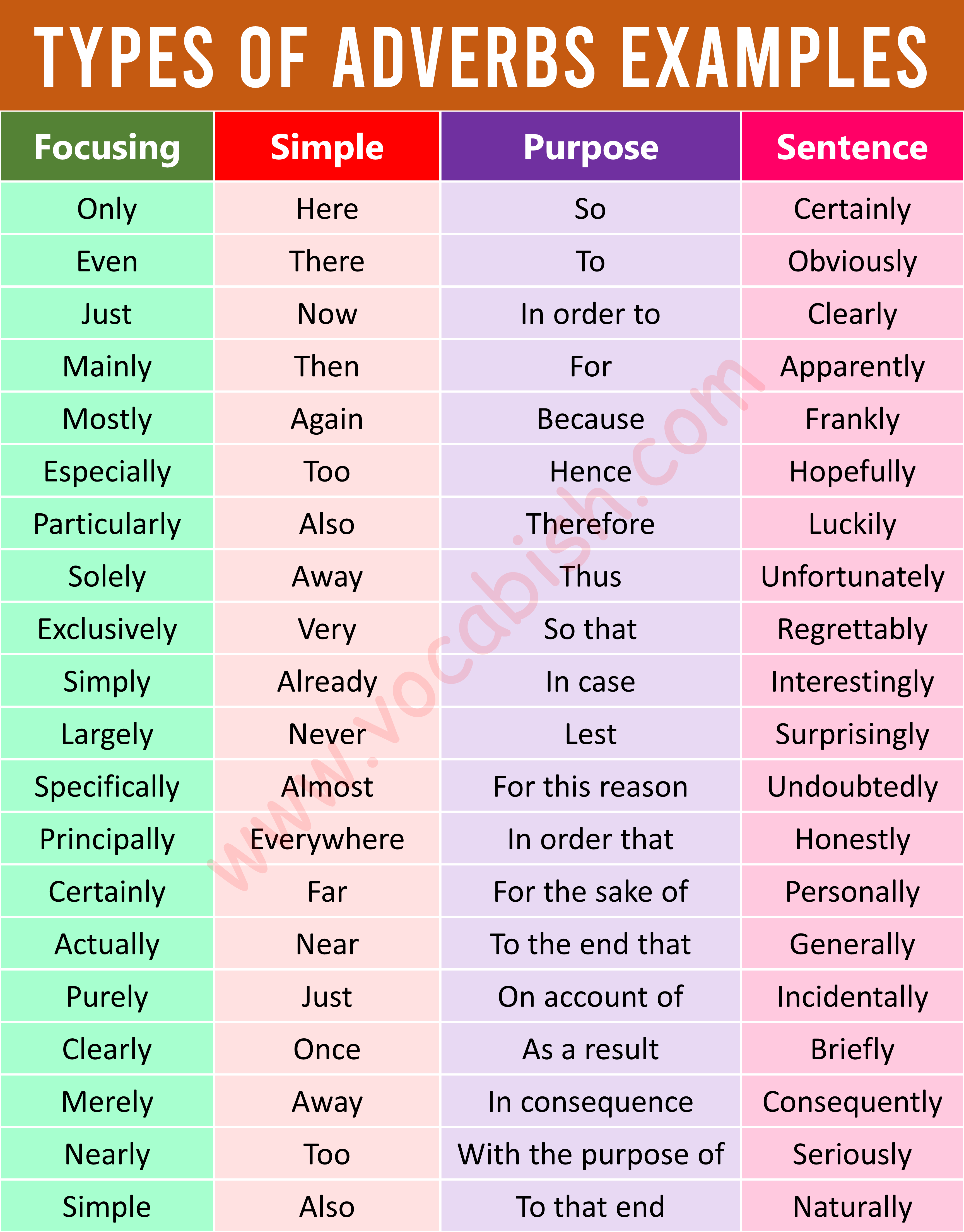
Focusing Adverb
- Only
- Even
- Just
- Mainly
- Mostly
- Especially
- Particularly
- Solely
- Exclusively
- Simply
- Largely
- Specifically
- Principally
- Certainly
- Actually
- Primarily
- Purely
- Clearly
- Merely
- Nearly
Simple Adverb
- Here
- There
- Now
- Then
- Again
- Too
- Also
- Thus
- Away
- Very
- Always
- Often
- Never
- Already
- Almost
- Everywhere
- Far
- Near
- Just
- Once
Adverb of Purpose
- So
- To
- In order to
- For
- Because
- Hence
- Therefore
- Thus
- So that
- In case
- Lest
- For this reason
- In order that
- For the sake of
- To the end that
- On account of
- As a result
- In consequence
- With the purpose of
- To that end
Sentence Adverb
- Certainly
- Obviously
- Clearly
- Apparently
- Frankly
- Hopefully
- Luckily
- Unfortunately
- Regrettably
- Interestingly
- Surprisingly
- Undoubtedly
- Honestly
- Personally
- Generally
- Incidentally
- Briefly
- Consequently
- Seriously
- Naturally
- Truthfully
- Evidently
- Thankfully
- Thankfully
- Remarkably
- Oddly
- Allegedly
- Specifically
- Ultimately
- Additionally
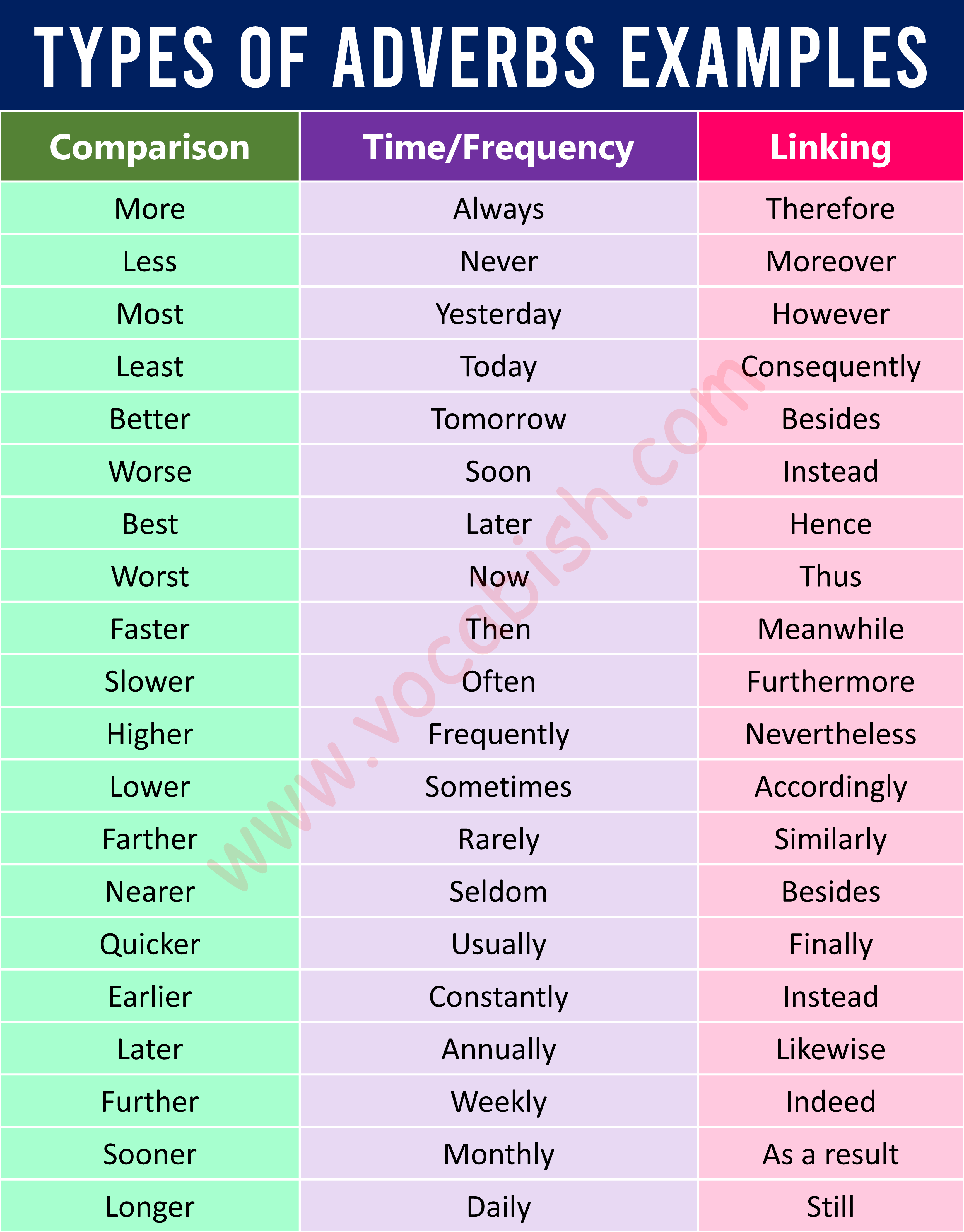
Adverb of Comparison
- More
- Less
- Most
- Least
- Better
- Worse
- Best
- Worst
- Faster
- Slower
- Higher
- Lower
- Farther
- Nearer
- Quicker
- Earlier
- Later
- Further
- Sooner
- Longer
Adverbs of Time/Frequency
- Always
- Never
- Yesterday
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Soon
- Later
- Now
- Then
- Often
- Frequently
- Sometimes
- Rarely
- Seldom
- Monthly
- Weekly
- Daily
- Annually
- Once
- Twice
- Thrice
- Again
- Before
- After
- Next
- Lately
- Recently
- Eventually
- Immediately
- Promptly
Linking Adverb
- Therefore
- Moreover
- However
- Consequently
- Besides
- Instead
- Hence
- Thus
- Meanwhile
- Furthermore
- Nevertheless
- Accordingly
- Similarly
- Subsequently
- Otherwise
- On the contrary
- Additionally
- In contrast
- Comparatively
- Conversely
- As a result
- In fact
- Indeed
- As a consequence
- Meanwhile
- Simultaneously
- In addition
- At the same time
- In the meantime
- Afterward
Learning adverb examples is a simple and effective way to make your English more expressive and clear. Adverbs help you describe actions, feelings, and situations more accurately — showing how, when, where, or how often something happens.
FAQs about List of Adverbs
What is an adverb with example?
An adverb is a word that describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
Example: She runs quickly.
Here, quickly tells how she runs.
What are 10 examples of adverbs?
Here are 10 common adverbs used in daily English:
Quickly, Slowly, Always, Never, Often, Today, Yesterday, Here, There, Very.
What is the rule of adverb in English grammar?
An adverb usually answers how, when, where, or how often something happens.
Example: He studies carefully (How?) / She came yesterday (When?).
What is the difference between adjective and adverb?
An adjective describes a noun → She is happy.
An adverb describes a verb or adjective → She sings happily.
How can I identify an adverb in a sentence?
Most adverbs end in –ly, but not all. Ask the question how, when, where, or how often after the verb.
Example: He drives fast. (How does he drive? → fast)
Read More