Learning medical prefixes and suffixes helps you understand complex medical terms and communicate clearly in English. In this blog post, you will explore common prefixes and suffixes used in medical vocabulary, along with their meanings and examples. Understanding these word parts improves your reading, writing, speaking, and listening skills, making it easier to interpret medical texts and communicate accurately in healthcare settings. By mastering medical prefixes and suffixes, you can decode unfamiliar terms and build confidence in medical English.
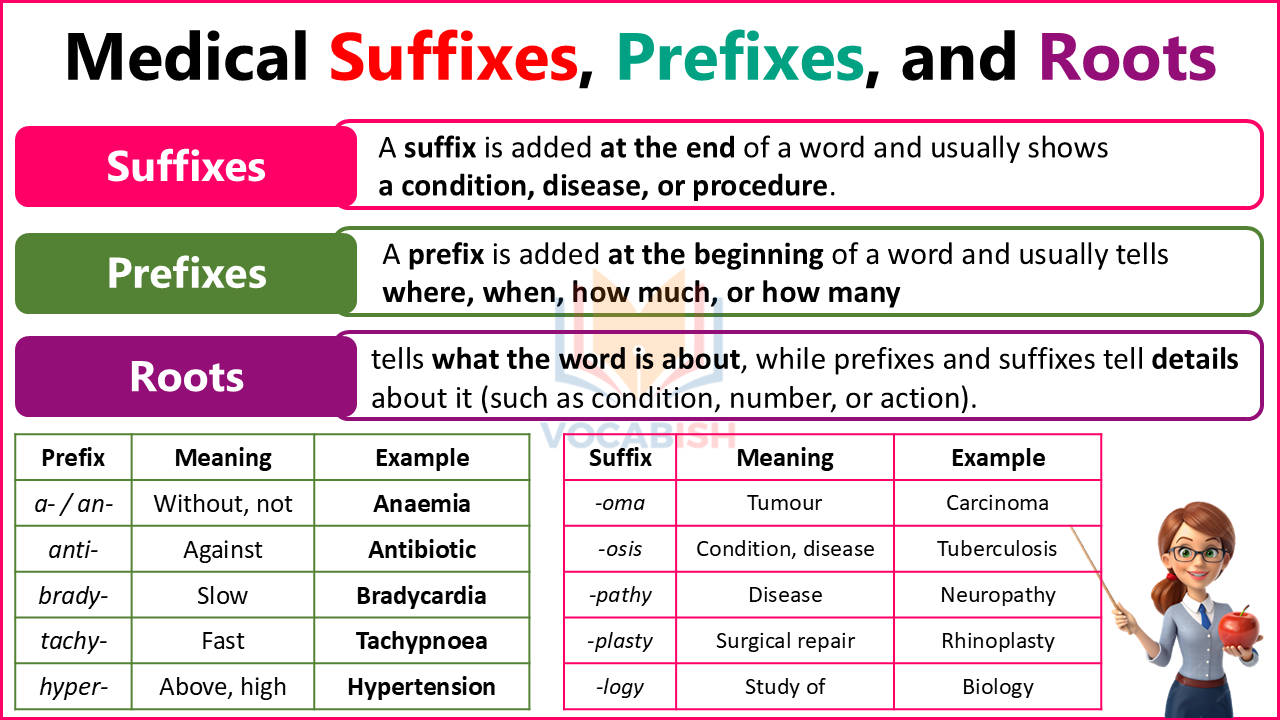
What Are Medical Prefixes and Suffixes?
In medical terminology, prefixes and suffixes are small parts added to words to change their meaning.
- A prefix is added at the beginning of a word and usually tells where, when, how much, or how many.
- A suffix is added at the end of a word and usually shows a condition, disease, or procedure.
Example:
Cardiology → Cardio (heart) + logy (study of) → Study of the heart
These word parts help create thousands of medical words that describe body parts, diseases, and treatments.
Why Are Prefixes and Suffixes Important?
Knowing medical prefixes and suffixes helps you:
- Understand complex medical words easily
- Remember meanings faster
- Communicate clearly in healthcare settings
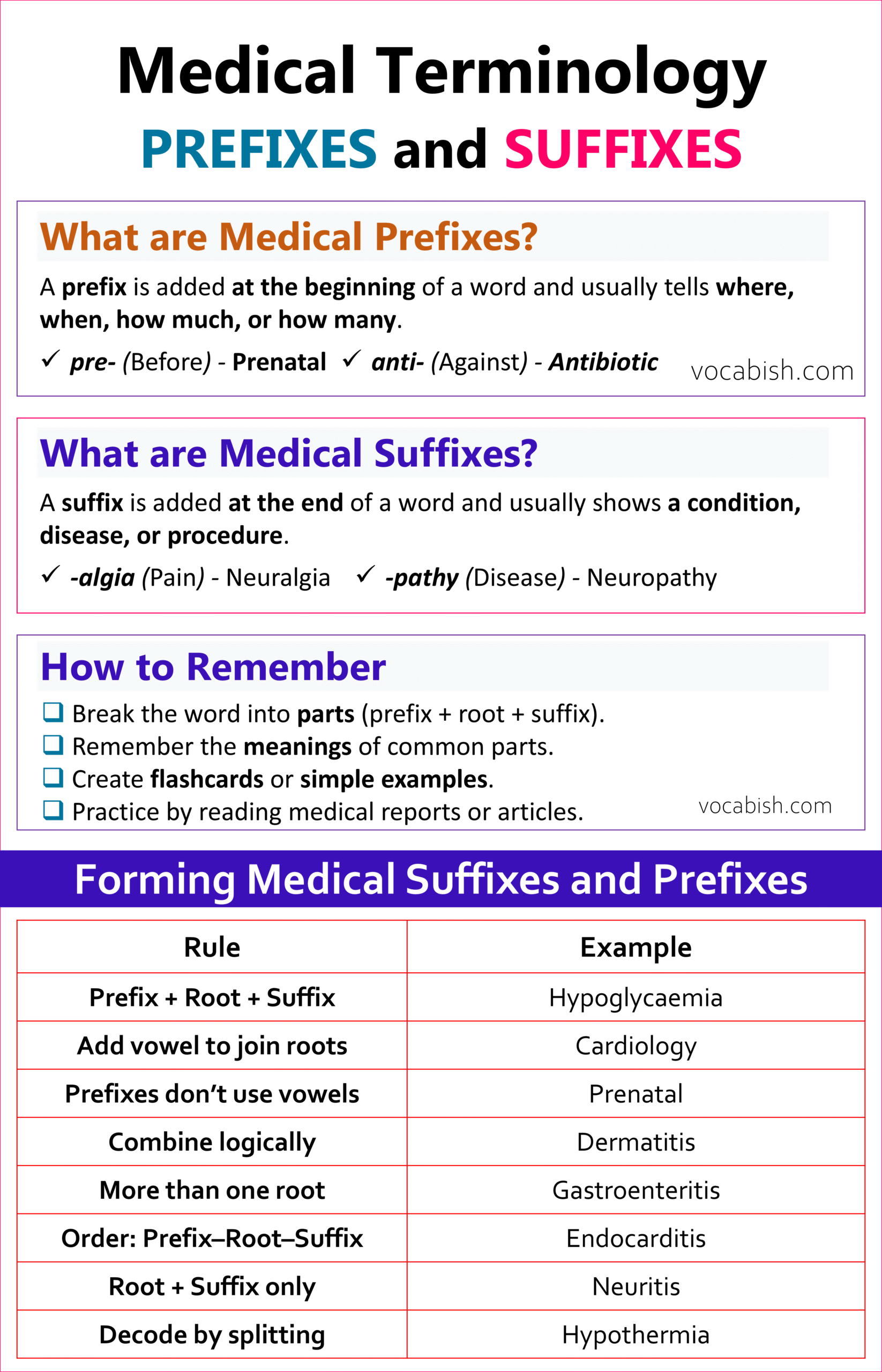
Rules for Forming Medical Prefixes and Suffixes
Let’s look at some easy and helpful rules to understand how these word parts join together.
Rule 1:
Prefix + Root + Suffix = Complete Medical Word
Most medical terms follow this simple structure.
Example:
Hypoglycaemia → Hypo (low) + glyc (sugar) + aemia (blood) → Low blood sugar
Rule 2:
Combining Vowels Are Used to Make Words Easier to Say
A combining vowel (usually “o” or sometimes “i”) is used to join word parts smoothly.
Example:
Cardi + o + logy → Cardiology → Study of the heart
Tip: Use the combining vowel when the suffix begins with a consonant, but not when it begins with a vowel.
Example:
- Gastr + o + logy ✅ (Gastroenterology)
- Gastr + itis ❌ (not Gastroitis, but Gastritis)
Rule 3:
Prefixes Don’t Need Combining Vowels
Prefixes are simply added before the root word.
Example:
Pre (before) + natal (birth) → Prenatal → Before birth
Post (after) + operative (surgery) → Postoperative → After surgery
Rule 4:
Keep the Meaning Logical
Each word part should make sense when combined.
Example:
Derm (skin) + itis (inflammation) → Dermatitis → Inflammation of skin
If you use the wrong combination, the meaning changes or becomes incorrect.
Rule 5:
Some Words Contain More Than One Root
Sometimes, a medical word has two or more roots joined by a vowel.
Example:
Gastr (stomach) + enter (intestine) + itis (inflammation) → Gastroenteritis → Inflammation of stomach and intestines
Rule 6:
The Order Matters
Prefixes come first, roots come next, and suffixes come last.
Example:
Endocarditis → Endo (inside) + card (heart) + itis (inflammation) → Inflammation inside the heart
Rule 7:
Some Terms Use Only Root + Suffix
Not all medical words have prefixes.
Example:
Neur (nerve) + itis (inflammation) → Neuritis → Nerve inflammation
Rule 8:
Use Word Meanings to Decode Unknown Terms
If you don’t know a medical word, split it into parts and translate each piece.
Example:
Hypo (low) + thermia (temperature) → Hypothermia → Low body temperature
Arthro (joint) + plasty (surgical repair) → Arthroplasty → Joint repair surgery
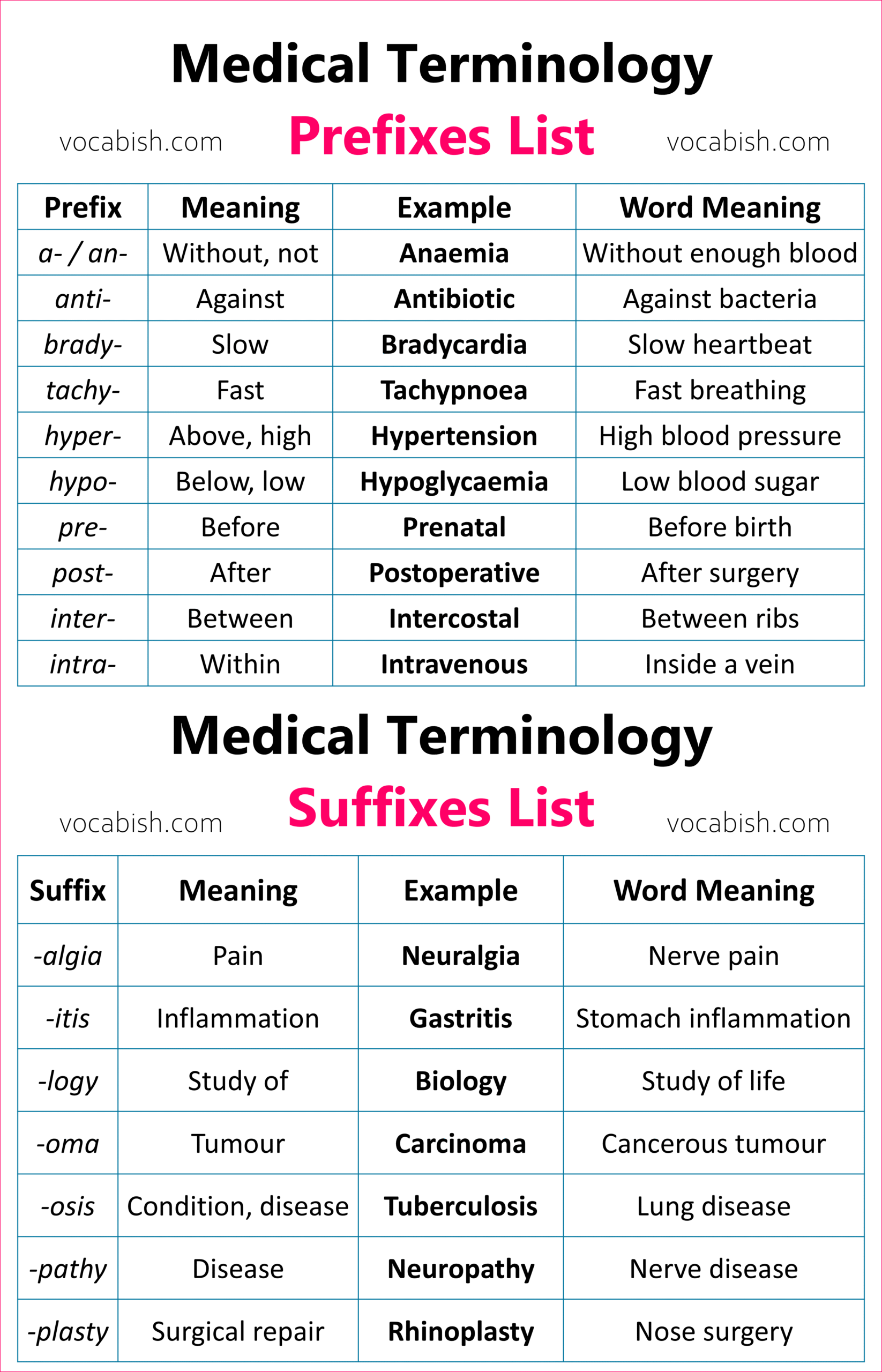
Medical Terminology Prefixes List
| Prefix | Meaning | Example | Word Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| a- / an- | Without, not | Anaemia | Without enough blood |
| anti- | Against | Antibiotic | Against bacteria |
| brady- | Slow | Bradycardia | Slow heartbeat |
| tachy- | Fast | Tachypnoea | Fast breathing |
| hyper- | Above, high | Hypertension | High blood pressure |
| hypo- | Below, low | Hypoglycaemia | Low blood sugar |
| pre- | Before | Prenatal | Before birth |
| post- | After | Postoperative | After surgery |
| inter- | Between | Intercostal | Between ribs |
| intra- | Within | Intravenous | Inside a vein |
Example:
Hypothermia → Hypo (low) + thermia (heat) → Low body temperature
Medical Terminology Suffixes List
| Suffix | Meaning | Example | Word Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| -algia | Pain | Neuralgia | Nerve pain |
| -itis | Inflammation | Gastritis | Stomach inflammation |
| -logy | Study of | Biology | Study of life |
| -ectomy | Surgical removal | Appendectomy | Removal of appendix |
| -oma | Tumour | Carcinoma | Cancerous tumour |
| -osis | Condition, disease | Tuberculosis | Lung disease |
| -pathy | Disease | Neuropathy | Nerve disease |
| -plasty | Surgical repair | Rhinoplasty | Nose surgery |
| -scope | Instrument for viewing | Microscope | Device to see small things |
| -uria | Condition of urine | Hematuria | Blood in urine |
Example:
Arthritis → Arthr (joint) + itis (inflammation) → Inflammation of joints
Medical Prefixes, Suffixes, and Roots List
Medical words often include a root word that shows the main meaning, with a prefix and suffix around it.
| Prefix | Root | Suffix | Full Word | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypo- | glyc (sugar) | -aemia | Hypoglycaemia | Low blood sugar |
| Cardi- | (heart) | -ology | Cardiology | Study of the heart |
| Neur- | (nerve) | -itis | Neuritis | Nerve inflammation |
| Derm- | (skin) | -ology | Dermatology | Study of the skin |
| Hepat- | (liver) | -megaly | Hepatomegaly | Enlarged liver |
Example:
Dermatitis → Derm (skin) + itis (inflammation) → Skin inflammation
How to Remember Medical Prefixes and Suffixes Easily
Here are a few quick tips to learn faster:
- Break the word into parts (prefix + root + suffix).
- Remember the meanings of common parts.
- Create flashcards or simple examples.
- Practice by reading medical reports or articles.
Example for Practice:
Biology → Bio (life) + logy (study of) → Study of life
Anaemia → An (without) + aemia (blood) → Lack of blood cells
In Short Words
Medical terminology prefixes and suffixes are the keys to understanding many medical terms. Once you know them, reading or hearing a long medical word becomes much easier. You can guess meanings even if you’ve never seen the word before!
Learning medical prefixes and suffixes is a smart and simple way to understand medical language. These small parts give big meanings to complex words. Whether you are a student, a healthcare learner, or just curious, mastering them will make medical terms easy, clear, and less scary!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are medical prefixes, suffixes, and roots?
Medical prefixes, suffixes, and roots are the main parts that form medical words.
- A prefix appears at the beginning and changes the meaning.
- A root gives the basic meaning of the word.
- A suffix comes at the end and often shows a condition or process.
Example: Cardiology → Cardi (heart) + logy (study of)
Why are prefixes, suffixes, and roots important in medical terminology?
They help explain complex medical terms easily. By understanding them, you can quickly guess the meaning of unfamiliar medical words and communicate more clearly in healthcare.
What are some common medical prefixes and their meanings?
Here are a few examples:
→ Hyper- = high or above
→ Hypo- = low or below
→ Brady- = slow
→ Tachy- = fast
→ Pre- = before
How do you form medical words using roots and suffixes?
You can create a medical word by combining a root and a suffix, sometimes with a combining vowel (o).
Example: Neur (nerve) + itis (inflammation) → Neuritis → Nerve inflammation
What is the difference between a root and a prefix in medical terms?
A root shows the main meaning (usually a body part or system), while a prefix adds extra information such as time, place, or number.
Example: Prenatal → Pre (before) + natal (birth)
Read More
- Abbreviations for Texting with Meanings
- Daily Used Household Item Names
- How to Introduce Yourself in English