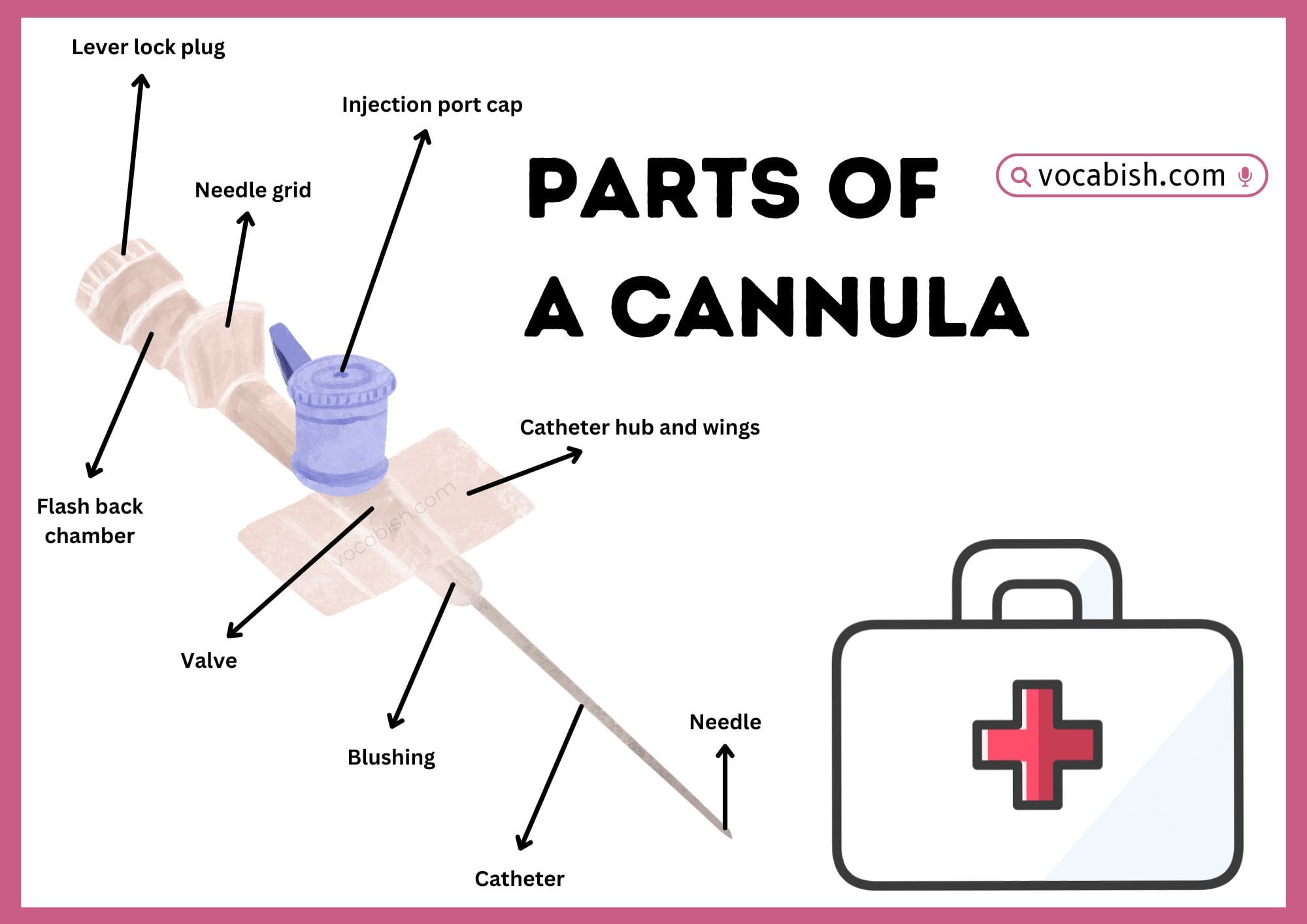
In this blog post, you will learn the different Parts of a Cannula, their Functions, and how they work together to safely deliver fluids or medications into the body. Understanding these parts helps you use a cannula correctly in medical, laboratory, or healthcare settings. When you know how each part works, your practical skills improve, and your understanding of intravenous procedures becomes stronger. You also improve your reading and comprehension because you can follow instructions, medical guides, and procedures confidently. Step by step, you will master the cannula and its safe use.
What is a Cannula?
A cannula is a thin medical tube inserted into a vein to give fluids, medicines, or take samples. It helps nurses and doctors work safely and quickly without using repeated needle injections. Once the cannula is in the vein, the plastic catheter stays inside while the needle is removed.
Main Parts of a Cannula
1. Needle
A sharp metal part used to enter the vein.
Function: Helps guide the plastic catheter into place.
2. Catheter (Plastic Tube)
A soft, thin tube that stays inside the vein after insertion.
Function: Carries fluids, medicines, or blood in and out of the body.
3. Hub
The coloured plastic connector at the end of the catheter.
Function: Helps connect syringes, IV lines, or caps. Also shows cannula size through colour coding.
4. Wings
Flat plastic tabs on the sides of the hub.
Function: Make it easier to hold, control, and tape the cannula to the skin.
6. Flashback Chamber
A small transparent chamber near the needle.
Function: Shows a flash of blood when the vein is reached, helping confirm correct placement.
7. Cap
A protective cover placed over the hub opening when no line is connected.
Function: Keeps the cannula clean and prevents infection.
Additional Cannula Features
Safety Shield
A built-in cover that hides the needle after use to prevent needle-stick injuries.
Colour Coding
Each cannula colour shows its size, such as pink, green, or blue, helping choose the right flow rate.
Backflow Preventer
Some cannulas include a valve that stops blood from flowing backwards.
Parts of Cannula Diagram
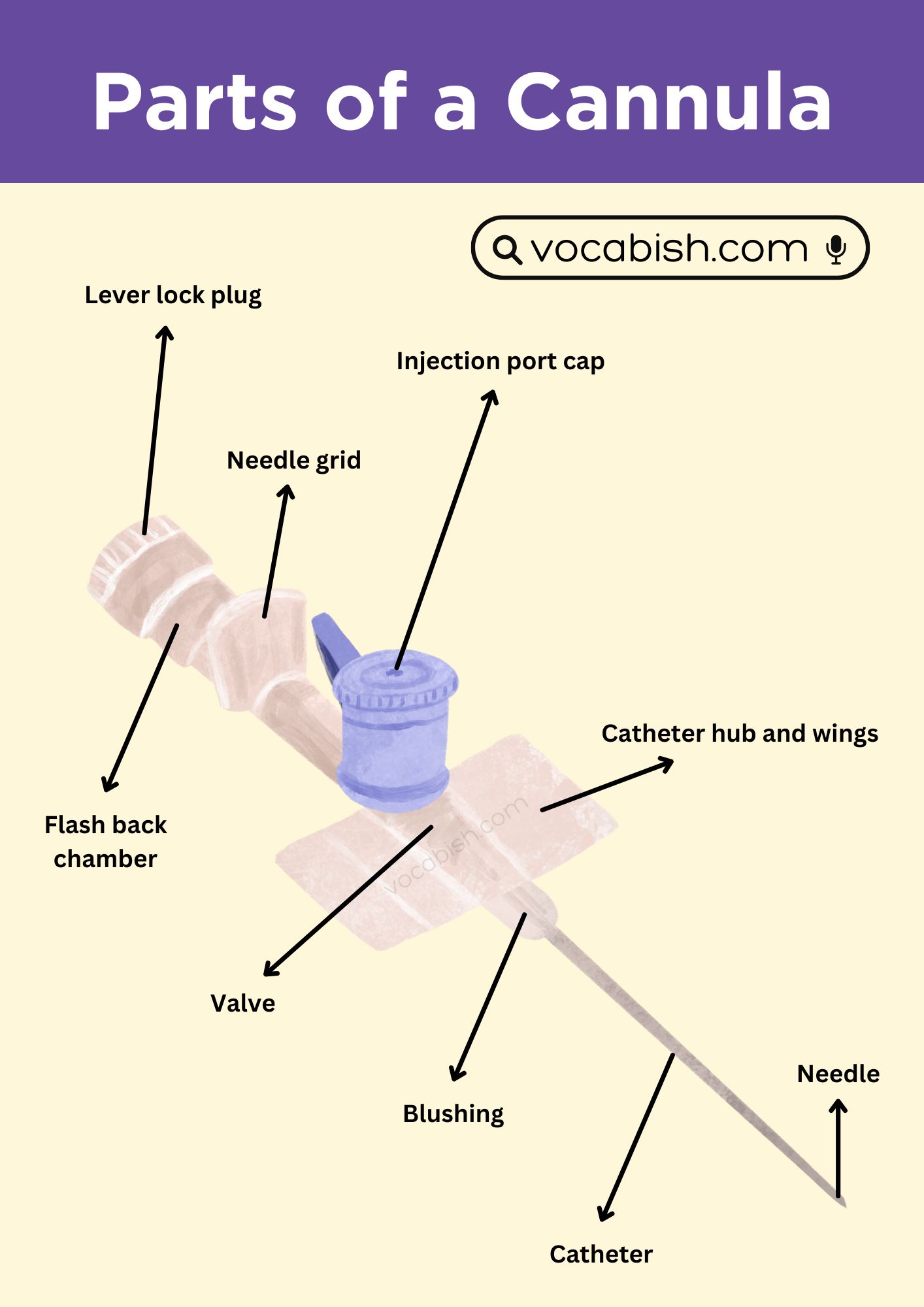
Cannula Parts and Their Functions
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Needle | Enters the vein and guides the catheter |
| Catheter | Stays inside the vein for fluid or medicine flow |
| Hub | Connects to IV lines and shows cannula size |
| Wings | Help hold and secure the cannula |
| Injection Port | Allows medicine to be given easily |
| Flashback Chamber | Shows blood to confirm correct placement |
| Cap | Protects the hub from germs |
| Safety Shield | Covers the needle after use |
How Each Part Helps in Use
- The needle finds the vein.
- The catheter stays inside for safe, long-term access.
- The hub connects the cannula to IV sets.
- The injection port allows extra medicine without a new needle.
- The flashback chamber confirms correct placement.
- The cap keeps the device safe when not in use.
FAQs
What are the main parts of a cannula?
The main parts are the needle, catheter, hub, wings, injection port, flashback chamber, and cap.
What does the catheter do in a cannula?
It stays inside the vein to carry fluids or medicines.
Why is the needle needed in a cannula?
It helps enter the vein and guides the plastic tube into place.
What is the function of the hub on a cannula?
It connects to syringes or IV lines and shows the size through colour coding.
What is the use of the injection port?
It lets medicines be given safely without removing the cannula.
Why does a cannula have wings?
They help control, place, and secure the cannula on the skin.
What is the flashback chamber for?
It shows a flash of blood to confirm the vein has been reached.
Why is the cap important on a cannula?
It covers the hub to protect against germs and infection.
What is a safety cannula?
It has a needle shield that closes automatically for safety.
Why are cannulas colour-coded?
Colours show different sizes to help choose the correct flow rate.
Read More