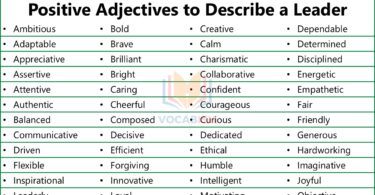
In this lesson, we are going to learn about pronouns in English. A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence. Instead of repeating the same noun over and over again, we use pronouns to make sentences shorter and easier to understand. There are different types of pronouns, each serving a different purpose in a sentence. By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Identify the different types of pronouns.
- Use pronouns correctly in sentences.
- Understand how pronouns help avoid repetition in speech and writing.
Let’s begin learning about pronouns and how they can make your sentences smoother and more natural!
Types of Pronouns
1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to people or things. They are divided into subject pronouns (who or what the sentence is about) and object pronouns (who or what receives the action).
- Subject Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
- Object Pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, us, them.
Examples:
- He is my best friend. (subject)
- I saw her at the mall. (object)
- They are going to the party. (subject)
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession of something.
- Examples: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs.
Examples:
- That book is mine.
- The house is theirs.
- Is this car yours?
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence. They end in -self or -selves.
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Examples:
- She made the cake herself.
- I hurt myself while running.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things. They are used to show whether something is near or far in distance or time.
- Examples: this, that, these, those.
Examples:
- This is my favorite book.
- Those are my shoes.
- That is a beautiful painting.
5. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to people, things, or amounts that are not specifically named. They do not refer to any particular person or thing.
- Examples: anyone, everyone, someone, nobody, something, anything.
Examples:
- Someone left their bag here.
- Everyone is invited to the party.
- Nobody knows the answer.
6. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns connect a clause or phrase to a noun or pronoun. They help add more information to the sentence.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that.
Examples:
- The boy who won the race is my brother.
- The book that I read was very interesting.
- The teacher whose car is parked outside is our math teacher.
Pronouns are an important part of English grammar because they make our sentences shorter, clearer, and less repetitive. By using different types of pronouns, we can replace nouns and make our writing and speech more natural. Now that you know the different types of pronouns, practice using them in your sentences to improve your English communication skills.
Read More