In this blog post, you will learn about regular and irregular verbs in English, with examples to help you understand how to use them correctly. Knowing these verbs can improve your speaking, reading, writing, and listening skills. By exploring verbs like walk, play, go, and have, you expand your vocabulary and gain confidence in forming sentences in English. Let’s master these verbs and use them effectively in everyday communication.
What are Regular and Irregular Verbs?
In English grammar, verbs are action words — they tell us what someone does.
Example: run, eat, play, sleep, study.
But verbs change their form when we talk about the past tense.
Based on this change, verbs are divided into two main types:
- Regular Verbs
- Irregular Verbs
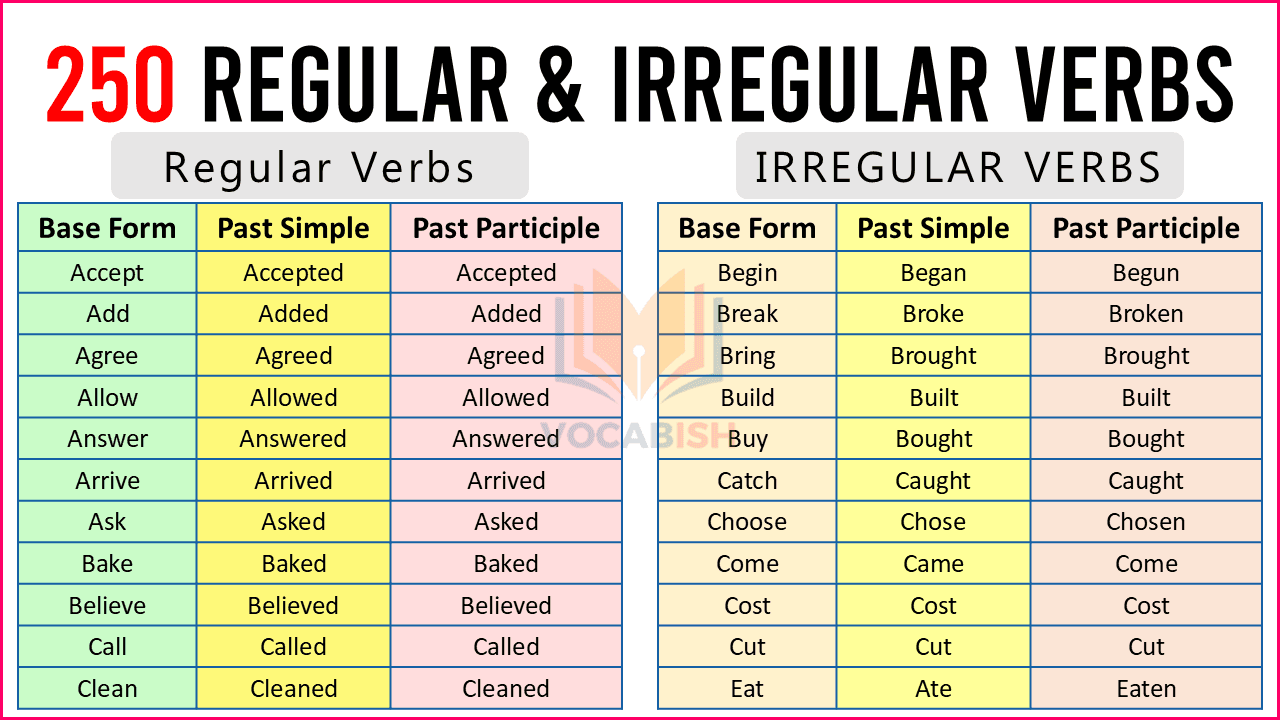
Regular Verbs
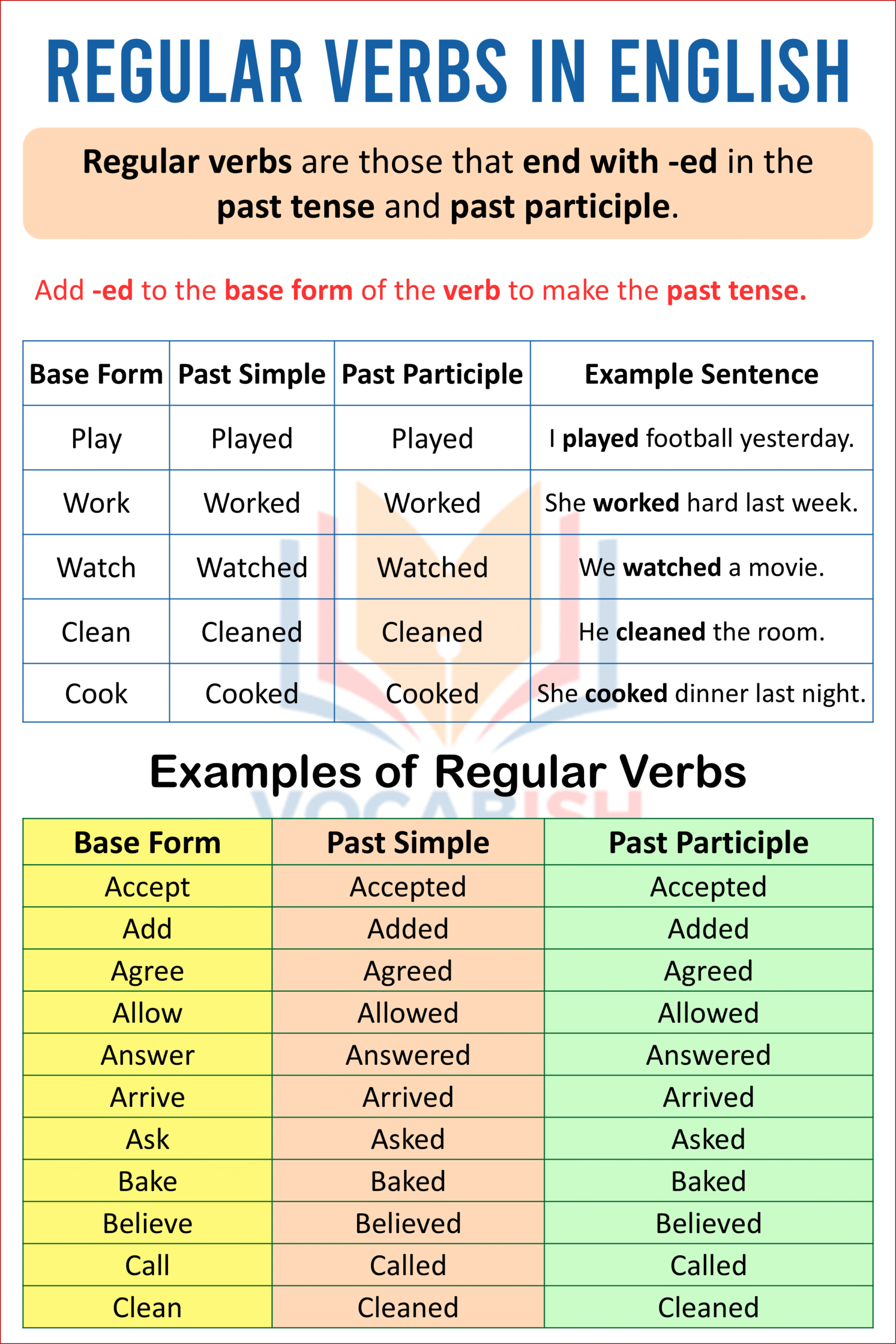
Regular verbs are those that end with -ed in the past tense and past participle.
- play → played → played
- talk → talked → talked
- work → worked → worked
Rule:
Add -ed to the base form of the verb to make the past tense.
Examples Table of Regular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Play | Played | Played | I played football yesterday. |
| Work | Worked | Worked | She worked hard last week. |
| Watch | Watched | Watched | We watched a movie. |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned | He cleaned the room. |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked | She cooked dinner last night. |
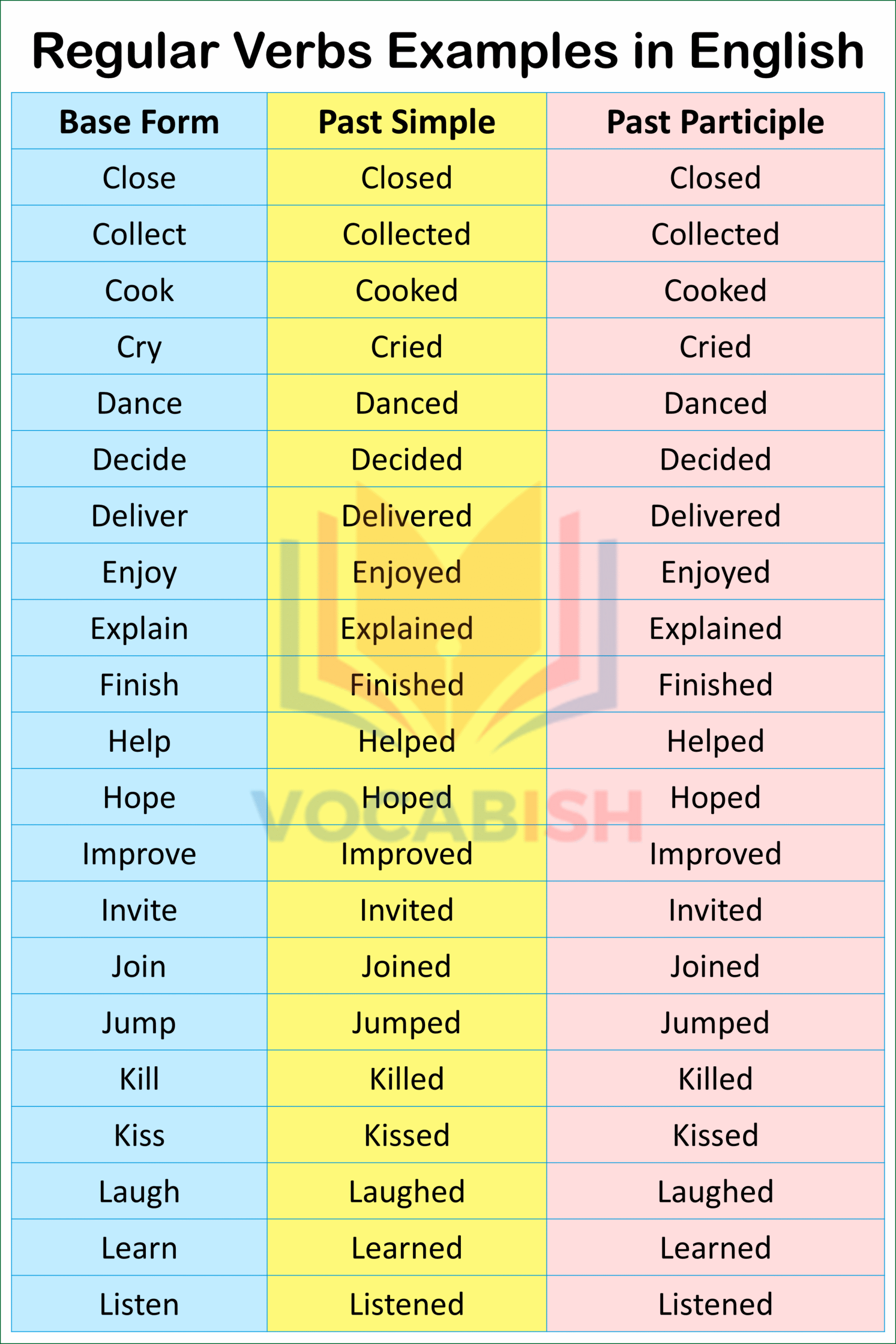
Regular Verbs Examples
Here’s the list of A to Z examples of regular verbs with their base, past simple, and past participle forms.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | Accepted | Accepted |
| Add | Added | Added |
| Agree | Agreed | Agreed |
| Allow | Allowed | Allowed |
| Answer | Answered | Answered |
| Arrive | Arrived | Arrived |
| Ask | Asked | Asked |
| Bake | Baked | Baked |
| Believe | Believed | Believed |
| Call | Called | Called |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned |
| Close | Closed | Closed |
| Collect | Collected | Collected |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked |
| Cry | Cried | Cried |
| Dance | Danced | Danced |
| Decide | Decided | Decided |
| Deliver | Delivered | Delivered |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed |
| Explain | Explained | Explained |
| Finish | Finished | Finished |
| Help | Helped | Helped |
| Hope | Hoped | Hoped |
| Improve | Improved | Improved |
| Invite | Invited | Invited |
| Join | Joined | Joined |
| Jump | Jumped | Jumped |
| Kill | Killed | Killed |
| Kiss | Kissed | Kissed |
| Laugh | Laughed | Laughed |
| Learn | Learned | Learned |
| Listen | Listened | Listened |
| Live | Lived | Lived |
| Look | Looked | Looked |
| Love | Loved | Loved |
| Marry | Married | Married |
| Need | Needed | Needed |
| Open | Opened | Opened |
| Paint | Painted | Painted |
| Plan | Planned | Planned |
| Play | Played | Played |
| Rain | Rained | Rained |
| Reach | Reached | Reached |
| Return | Returned | Returned |
| Share | Shared | Shared |
| Show | Showed | Showed |
| Smile | Smiled | Smiled |
| Start | Started | Started |
| Stay | Stayed | Stayed |
| Study | Studied | Studied |
| Talk | Talked | Talked |
| Thank | Thanked | Thanked |
| Travel | Travelled | Travelled |
| Use | Used | Used |
| Visit | Visited | Visited |
| Wait | Waited | Waited |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Wash | Washed | Washed |
| Watch | Watched | Watched |
| Work | Worked | Worked |
Irregular verbs do not follow the regular -ed rule. Their past forms change completely or stay the same.
- go → went → gone
- eat → ate → eaten
- come → came → come
These verbs must be memorised because they don’t follow a pattern.
Examples Table of Irregular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Go | Went | Gone | She went to school. |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten | I have eaten breakfast. |
| See | Saw | Seen | We saw a rainbow. |
| Write | Wrote | Written | He has written a story. |
| Take | Took | Taken | She took her bag. |
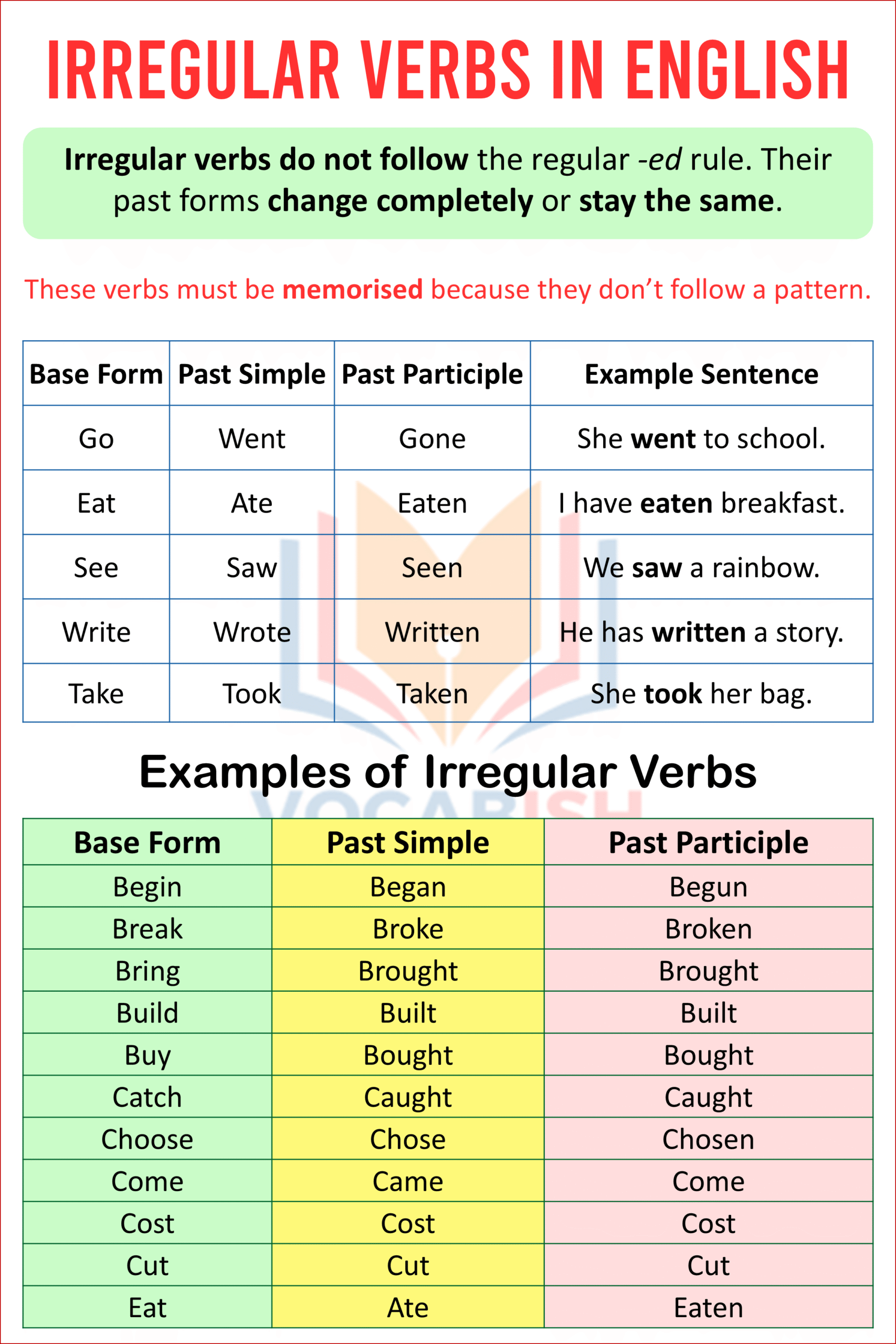
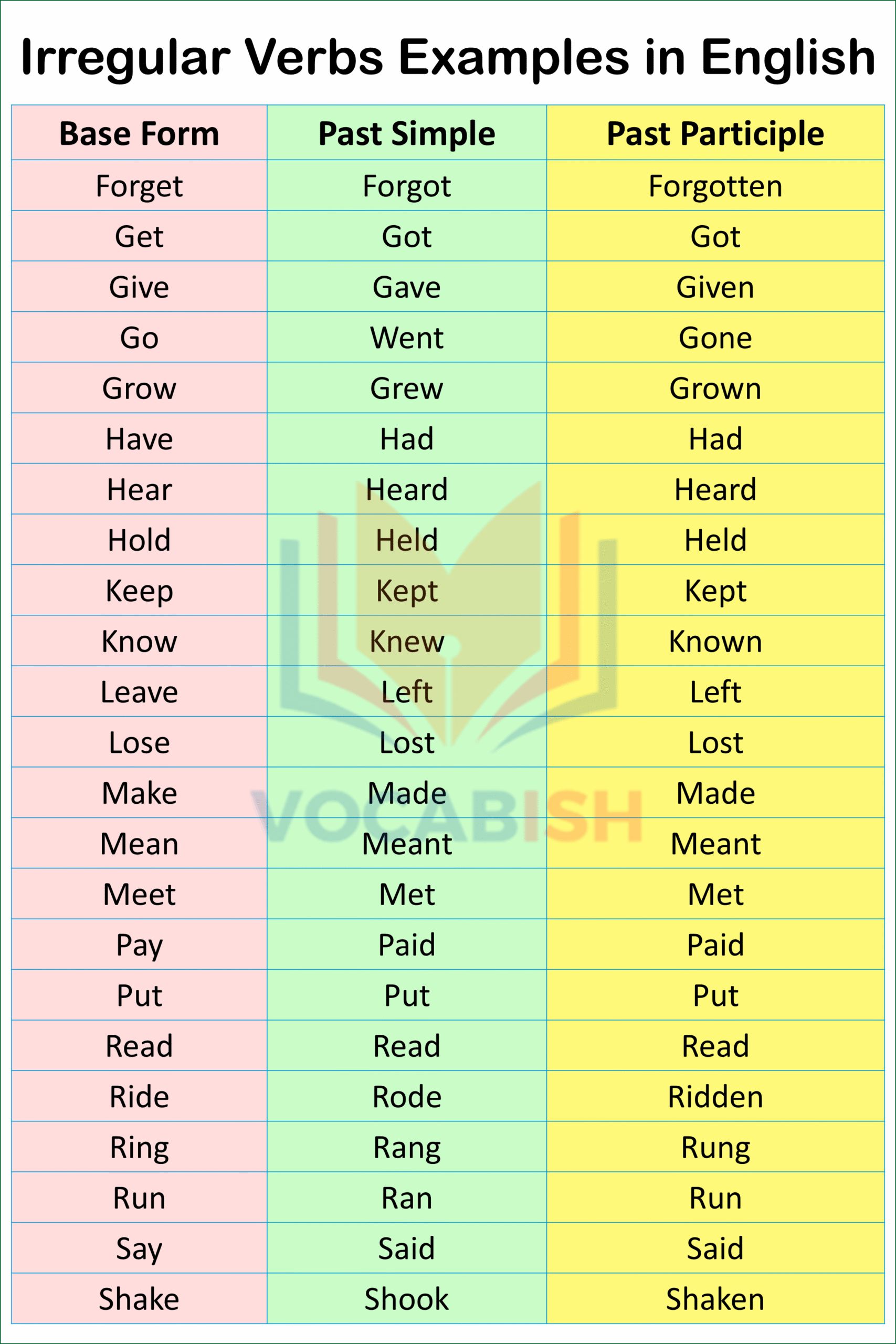
Irregular Verbs Examples
Here’s the list of A to Z examples of irregular verbs with their base, past simple, and past participle forms in English.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Begin | Began | Begun |
| Break | Broke | Broken |
| Bring | Brought | Brought |
| Build | Built | Built |
| Buy | Bought | Bought |
| Catch | Caught | Caught |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen |
| Come | Came | Come |
| Cost | Cost | Cost |
| Cut | Cut | Cut |
| Do | Did | Done |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk |
| Drive | Drove | Driven |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen |
| Feel | Felt | Felt |
| Find | Found | Found |
| Fly | Flew | Flown |
| Forget | Forgot | Forgotten |
| Get | Got | Got |
| Give | Gave | Given |
| Go | Went | Gone |
| Grow | Grew | Grown |
| Have | Had | Had |
| Hear | Heard | Heard |
| Hold | Held | Held |
| Keep | Kept | Kept |
| Know | Knew | Known |
| Leave | Left | Left |
| Lose | Lost | Lost |
| Make | Made | Made |
| Mean | Meant | Meant |
| Meet | Met | Met |
| Pay | Paid | Paid |
| Put | Put | Put |
| Read | Read | Read |
| Ride | Rode | Ridden |
| Ring | Rang | Rung |
| Run | Ran | Run |
| Say | Said | Said |
| See | Saw | Seen |
| Sell | Sold | Sold |
| Send | Sent | Sent |
| Shake | Shook | Shaken |
| Shine | Shone | Shone |
| Shoot | Shot | Shot |
| Show | Showed | Shown |
| Sing | Sang | Sung |
| Sit | Sat | Sat |
| Sleep | Slept | Slept |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken |
| Spend | Spent | Spent |
| Stand | Stood | Stood |
| Swim | Swam | Swum |
| Take | Took | Taken |
| Teach | Taught | Taught |
| Tell | Told | Told |
| Think | Thought | Thought |
| Throw | Threw | Thrown |
| Understand | Understood | Understood |
| Wake | Woke | Woken |
| Wear | Wore | Worn |
| Win | Won | Won |
| Write | Wrote | Written |
Both types of verbs are used to talk about past actions. The main difference is how their form changes.
Examples:
Regular Verbs:
- clean → cleaned → cleaned → I cleaned the house.
- help → helped → helped → They helped their friend.
Irregular Verbs:
- go → went → gone → She went to the park.
- eat → ate → eaten → We have eaten lunch.
Regular and irregular verbs are the foundation of English grammar. Regular verbs are simple — just add -ed, while irregular verbs need to be memorised. Learning them helps you speak and write English correctly and confidently.
FAQs
What are regular and irregular verbs in English grammar?
Regular verbs are verbs that form their past tense by adding -ed (like play → played), while irregular verbs change their form completely or stay the same (like go → went → gone).
What is the main difference between regular and irregular verbs?
The main difference is that regular verbs follow a rule and end in -ed in the past tense, while irregular verbs do not follow this rule and change in different ways.
What are 10 examples of regular and irregular verbs?
Regular verbs: play–played, work–worked, talk–talked, help–helped, clean–cleaned.
Irregular verbs: go–went, eat–ate, come–came, see–saw, write–wrote.
How can I easily learn irregular verbs in English?
You can learn irregular verbs by grouping similar ones, practising daily, and using them in short sentences. Repetition and reading help you remember their forms easily.
Why is it important to learn regular and irregular verbs?
Learning regular and irregular verbs helps you speak and write English correctly, especially when talking about past actions and daily experiences.
Read More