In this blog post, you will learn the parts, functions, and diagram of an egg in English. This vocabulary helps you understand the names of each part of an egg and what role it plays. Learning these words is important for students, science learners, and English learners who want to describe objects and biology accurately. When you know these terms, you can speak confidently about eggs, read science texts with better understanding, write clear descriptions, and follow spoken explanations more easily. Keep reading to build your knowledge and understand how each part of an egg works together.
What is an Egg?
An egg is a natural food and a living structure made by birds. It protects and feeds a baby bird before it hatches. In daily life, eggs are also used for cooking, baking, and nutrition.
In English, the word egg can be used in different ways:
- Food: I eat an egg for breakfast.
- Science: The egg contains a developing chick.
- Expression: He put all his eggs in one basket.
Main Parts of an Egg
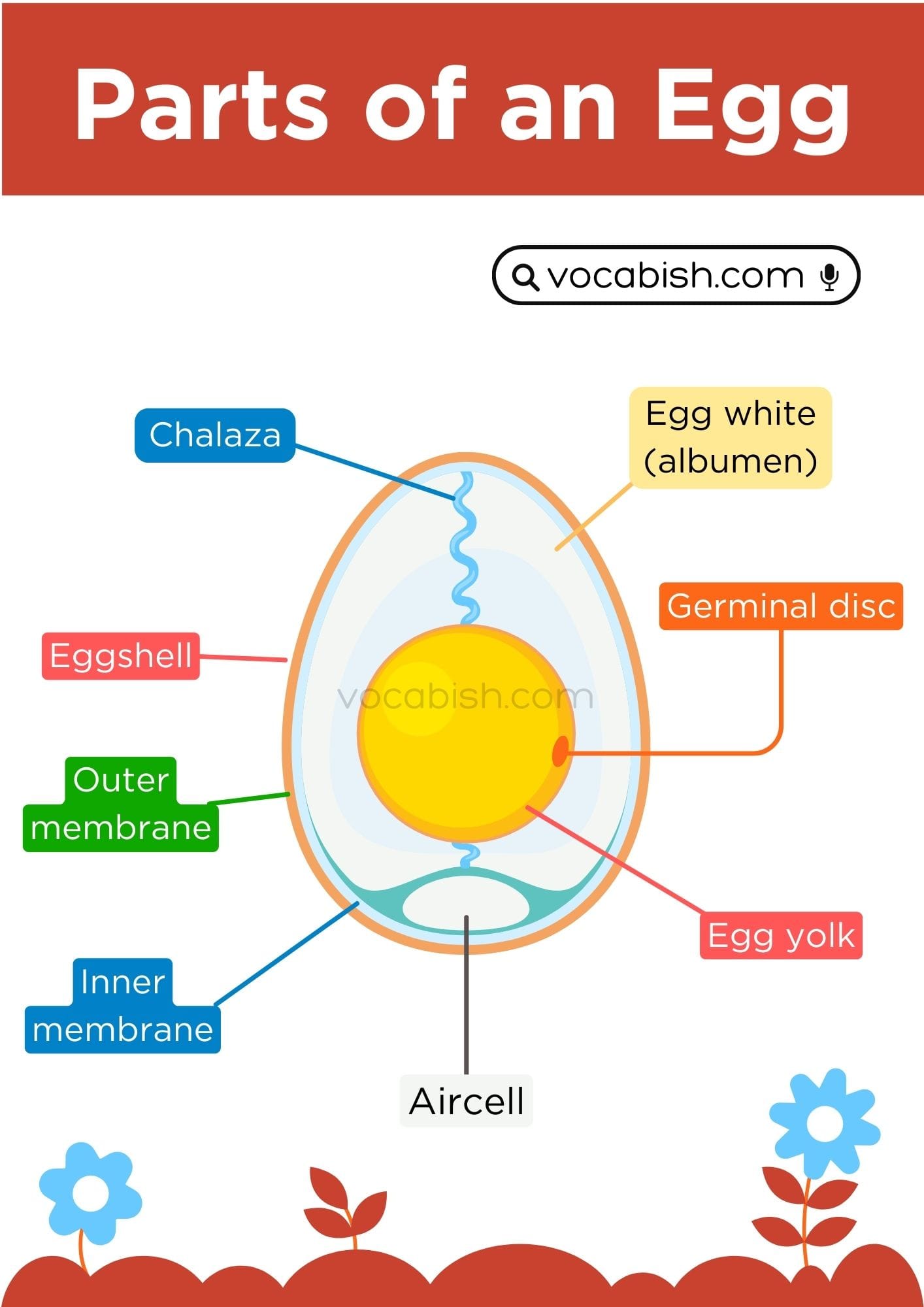
Eggshell
Eggshell
The hard outer cover of the egg.
Functions:
- Protects the inside of the egg
- Made mostly of calcium
- Has tiny pores to let air pass
Eggshell Membranes
Outer membrane
Thin layer just inside the shell.
Inner membrane
Second thin layer under the outer one.
Functions:
- Both membranes help stop bacteria
- They add extra protection
Inner Parts of an Egg
Egg White (Albumen)
Egg white (albumen): The clear liquid around the yolk.
Functions:
- Protects the yolk
- Contains protein
- Turns white when cooked
Egg Yolk
Egg yolk: The yellow centre of the egg.
Functions:
- Stores food for the chick
- Rich in vitamins and fat
- Gives colour and flavour in cooking
Supporting Structures of an Egg
Chalaza
Chalaza: Two twisted white strings inside the egg.
Functions:
- Hold the yolk in the centre
- Keep the yolk steady
Air Cell
Air cell: A small pocket of air at the wide end of the egg.
Functions:
- Forms after the egg is laid
- Grows larger as the egg gets older
Germinal Disc
Germinal disc: A tiny white spot on the yolk.
Functions:
- Where a chick can start to grow
- Not visible unless you look closely
List of Egg Parts and Their Functions
Outer Parts
- Eggshell: Hard cover that protects the egg
- Outer membrane: First thin protective layer
- Inner membrane: Second protective layer under the shell
Inner Parts
- Egg white (albumen): Protects yolk and provides protein
- Egg yolk: Food source and main nutrient store
Supporting Parts
- Chalaza: Keeps the yolk in the centre
- Air cell: Stores air for the developing chick
- Germinal disc: Starting point of chick development
Parts of an Egg Diagram
Summary on Parts of an Egg
The parts of an egg work together to protect and support life. From the strong shell to the nutrient-rich yolk, each part has a clear function. Understanding these parts helps students learn science, improve vocabulary, and understand food better in daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main parts of an egg?
The main parts of an egg are the eggshell, eggshell membranes, egg white (albumen), egg yolk, chalaza, air cell, and germinal disc. Each part has a role in protection, nutrition, or support.
What is the function of the eggshell?
The eggshell protects the egg from damage and germs. It is hard, made of calcium, and has tiny pores that allow air to pass.
What does the egg white do?
The egg white (albumen) surrounds the yolk and protects it. It also provides protein and water for the developing chick.
Why is the egg yolk important?
The egg yolk stores food and nutrients. It contains fats, vitamins, and energy needed for growth.
What is the chalaza in an egg?
The chalaza is a twisted, white strand that holds the yolk in the centre of the egg and keeps it stable.
What is the air cell in an egg?
The air cell is a small pocket of air at the wide end of the egg. It helps the chick breathe before hatching and grows as the egg ages.
What is the germinal disc?
The germinal disc is a small white spot on the yolk where a chick can begin to develop if the egg is fertilised.
Read More
- Parts of a Fish and Their Functions
- Parts of a Mushroom Their Functions
- All Parts of a Tree Names and Functions
