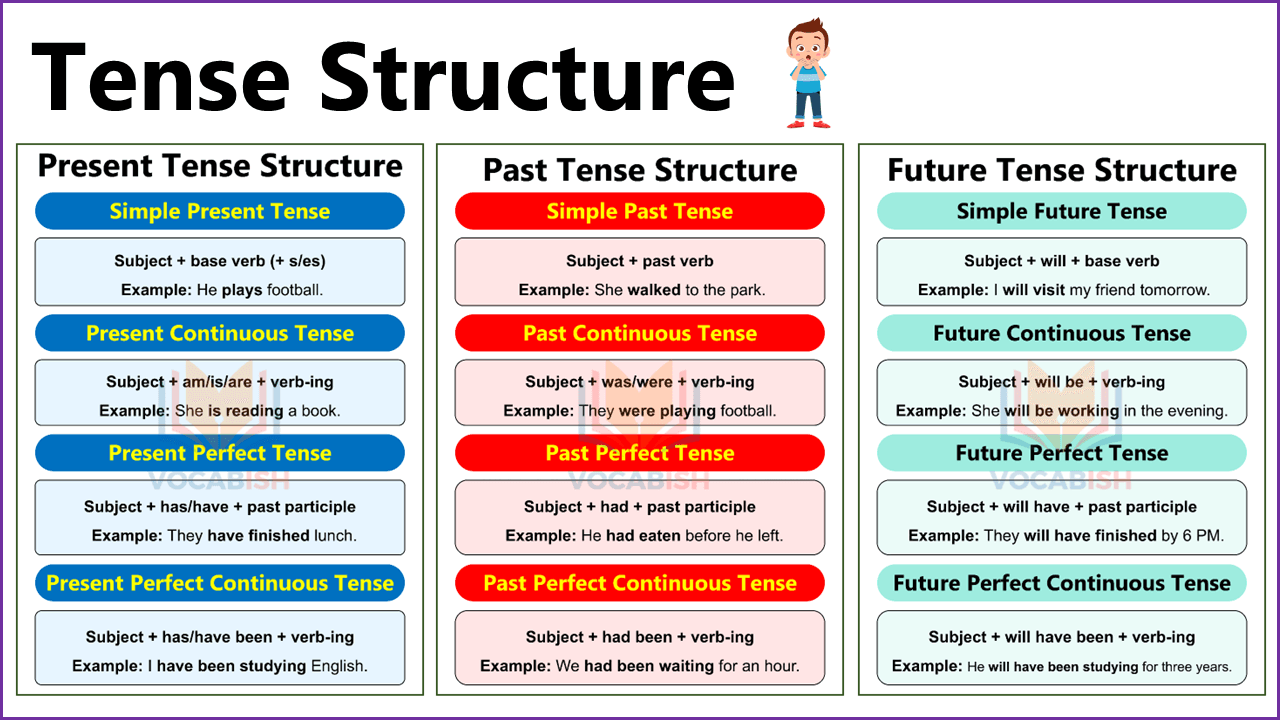
Understanding tenses is one of the most important parts of learning English grammar. Tenses show the time of an action — whether it happens now, before now, or later. In this lesson, you will learn the structure and use of present, past, and future tenses with examples and tables that make learning simple and fast.
What Are Tenses?
A tense shows when something happens. English has three main tenses — Present, Past, and Future. Each tense tells if the action happens today, yesterday, or tomorrow.
Tense Structure
Tense structure in English grammar helps us show when an action happens — in the present, past, or future. Each tense has its own form and rule that changes the verb to express time clearly. Learning tense structure makes it easier to speak, write, and understand English sentences correctly.
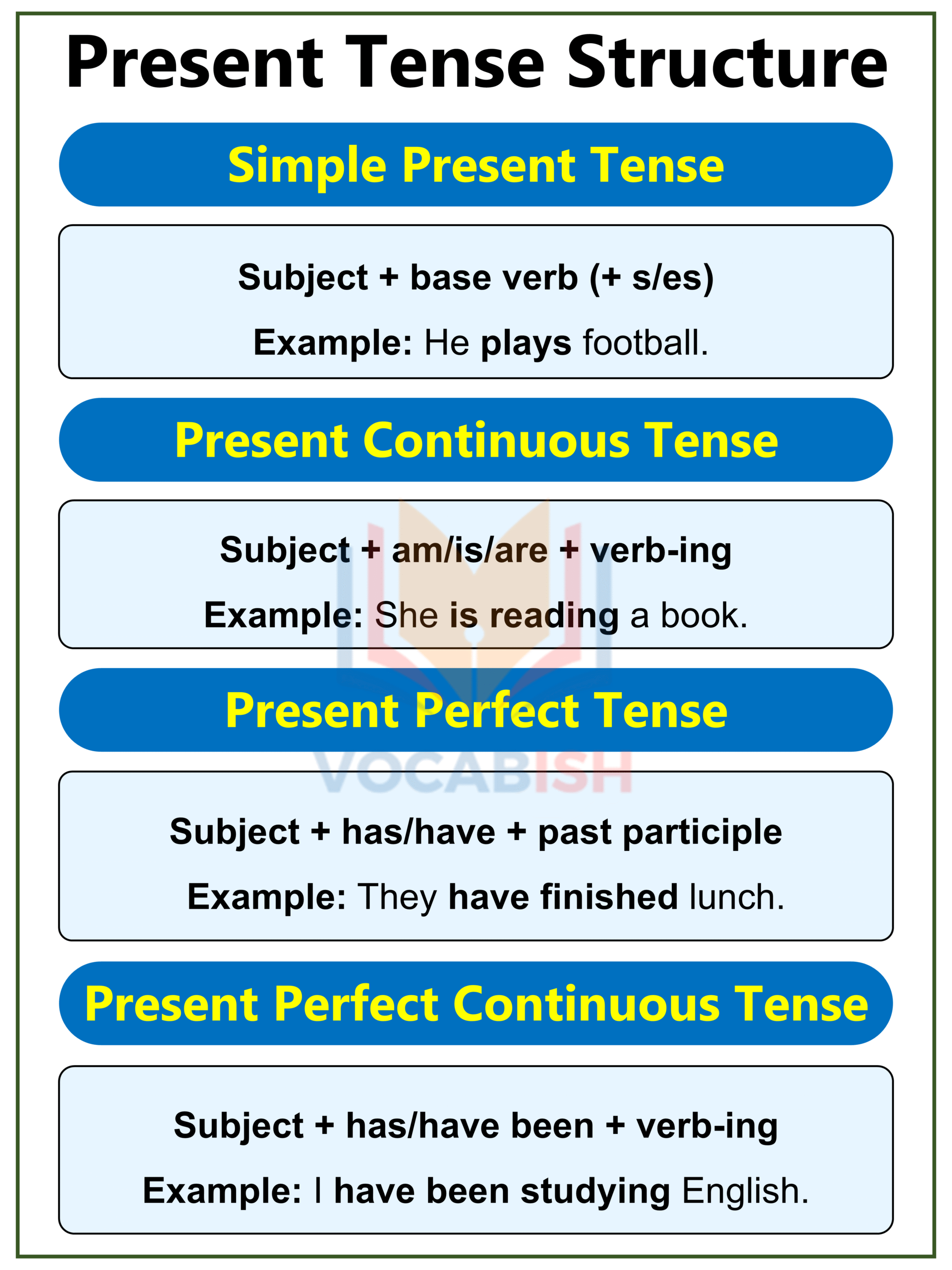
Present Tense Structure
The Present Tense talks about what is happening now, always true, or done regularly.
| Form | Structure | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | Subject + base verb (+ s/es) | He plays football. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing | She is reading a book. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + past participle | They have finished lunch. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + has/have been + verb-ing | I have been studying English. |
- I go to school every day.
- She is cooking dinner now.
- We have completed our homework.
- He has been working since morning.
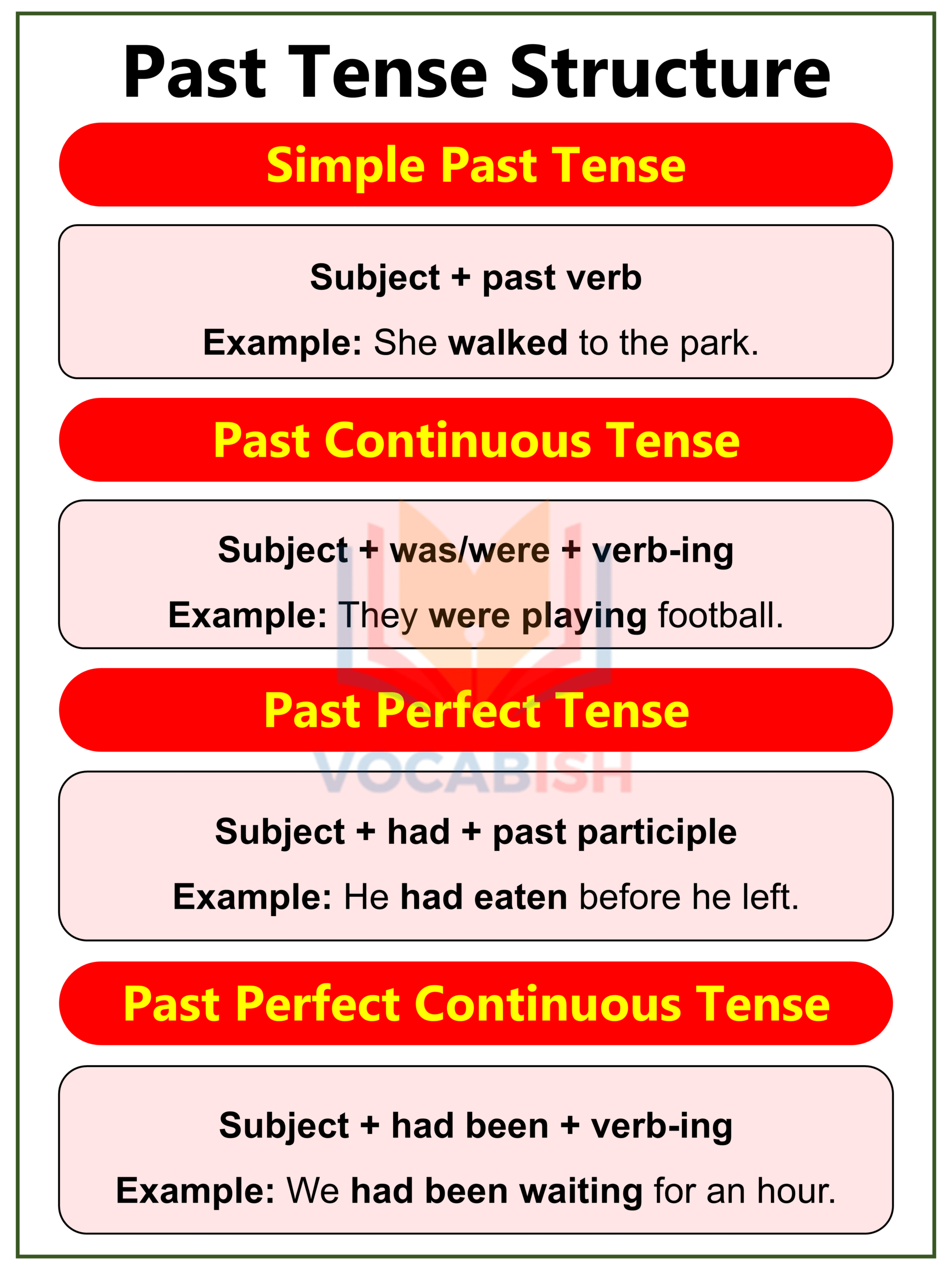
Past Tense Structure
The Past Tense describes actions that already happened. It tells us what someone did or what happened in the past.
| Form | Structure | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | Subject + past verb | She walked to the park. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb-ing | They were playing football. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle | He had eaten before he left. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + verb-ing | We had been waiting for an hour. |
- I watched a film yesterday.
- They were talking all night.
- She had studied before the exam.
- We had been living there for years.
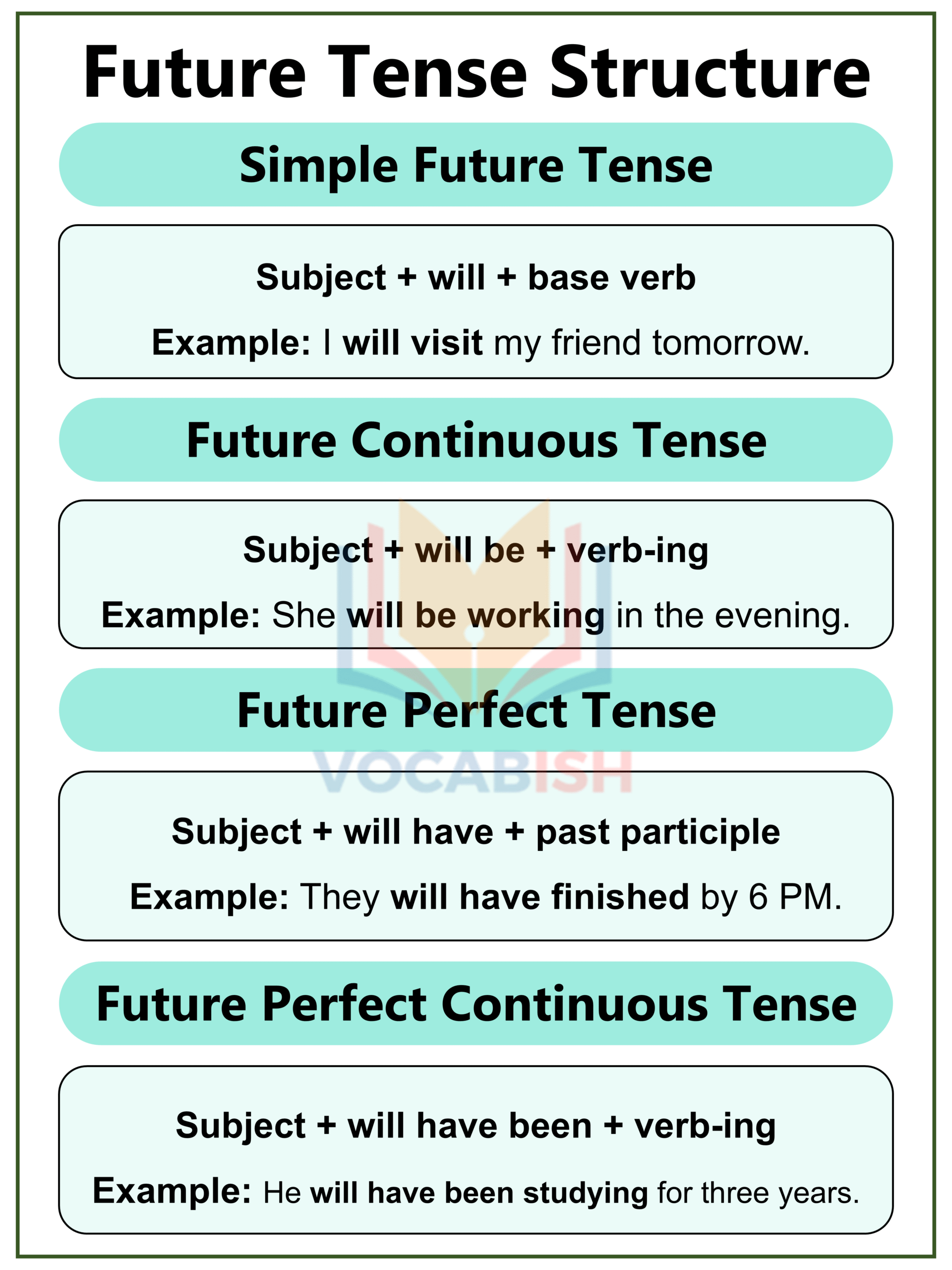
Future Tense Structure
The Future Tense shows what will happen later or is planned to happen.
| Form | Structure | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Future | Subject + will + base verb | I will visit my friend tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be + verb-ing | She will be working in the evening. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will have + past participle | They will have finished by 6 PM. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb-ing | He will have been studying for three years. |
- I will call you later.
- She will be travelling next week.
- We will have completed the project by Friday.
- They will have been living here for ten years.
How to Remember Tenses Easily
- Think of Time → Past = before, Present = now, Future = later.
- Use Signal Words → yesterday, now, tomorrow help find the tense.
- Look at the Verb → changes in verb forms show time.
- Practise Daily → write short sentences for each tense.
Learning tense structure helps you speak and write correctly in English. When you understand how tenses work, you can easily describe time, actions, and plans. Keep practising these forms and examples every day to master English grammar step by step.
FAQs about Tense Structure
What is the structure of the Simple Present Tense?
The structure is: Subject + base verb (add s/es for he, she, it).
Example: He plays football every day.
What is the structure of the Present Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing.
Example: She is watching TV.
What is the structure of the Present Perfect Tense?
The structure is: Subject + has/have + past participle (verb-3).
Example: They have finished their work.
What is the structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + has/have been + verb-ing.
Example: I have been studying English for two years.
What is the structure of the Simple Past Tense?
The structure is: Subject + past form of verb (verb-2).
Example: She walked to school.
What is the structure of the Past Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + was/were + verb-ing.
Example: They were playing football.
What is the structure of the Past Perfect Tense?
The structure is: Subject + had + past participle (verb-3).
Example: He had eaten breakfast before going out.
What is the structure of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + had been + verb-ing.
Example: We had been waiting for an hour.
What is the structure of the Simple Future Tense?
The structure is: Subject + will + base verb.
Example: I will travel tomorrow.
What is the structure of the Future Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + will be + verb-ing.
Example: She will be working this evening.
What is the structure of the Future Perfect Tense?
The structure is: Subject + will have + past participle (verb-3).
Example: They will have finished by 6 PM.
What is the structure of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense?
The structure is: Subject + will have been + verb-ing.
Example: He will have been studying for three years.
Read More